Impact of Three Strengthening Exercises on Dynamic Knee Valgus and Balance with Poor Knee Control among Young Football Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34068810
- PMCID: PMC8151944
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9050558
Impact of Three Strengthening Exercises on Dynamic Knee Valgus and Balance with Poor Knee Control among Young Football Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
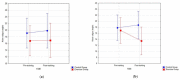
The observed dynamic knee valgus and the limited dynamic balance described in the literature are modifiable risk factors for injuries in athletes. Therefore, identification and appropriate prevention are crucial in managing the development of young athletes. The aim of the study was to assess the effectiveness of three exercises strengthening the muscles: gluteal medius, popliteal and tibialis posterior to reduce dynamic knee valgus and improve the dynamic balance of the lower limbs in young football players with poor knee control. A total of 134 footballers were assessed for eligibility, and finally 45 participants (age 12-15) met the inclusion criteria. Participants were assessed with 2D video kinematic analysis during single-leg squats to assess the knee valgus angles and the dynamic balance (Y-Balance Test). No significant interactions between groups (Control and Exercise) and time (baseline and after 6 week) were noted for dynamic valgus for the left and right knee (p > 0.05). For the dynamic balance, there were statistically significant results, but not clinically relevant for anterior, posteromedial, and composite direction for the right lower limbs and for the anterior direction for left lower limbs in the exercise group. However, there were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in all of the YBT scores for both lower limbs between groups. This study demonstrated that there were no statistically significant differences in dynamic knee valgus angles and dynamic balance values after 6 weeks of exercise program in young footballers with poor knee control. Future randomized trials should focus on more comprehensive exercises, where possible using biofeedback methods to improve knee kinematics.
Keywords: Y-Balance test; injury prevention; knee kinetics; medial knee displacement; single leg squat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effectiveness of the STOP-X training program on the knee valgus angle and balance in female basketball players with dynamic knee valgus: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 Feb 21;16(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00844-2. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38383435 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Stop X exercises on balance, strength and range of motion of male adolescent football players with dynamic knee valgus.Sci Rep. 2025 May 25;15(1):18213. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00840-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40414920 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of gluteus medius and tibialis anterior kinesio taping on postural control, knee kinematics, and knee proprioception in female athletes with dynamic knee valgus.Phys Ther Sport. 2022 Jan;53:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2021.11.010. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Phys Ther Sport. 2022. PMID: 34875529 Clinical Trial.
-
Dynamic Knee Valgus in Single-Leg Movement Tasks. Potentially Modifiable Factors and Exercise Training Options. A Literature Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 6;17(21):8208. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218208. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33172101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence-based concepts for prevention of knee and ACL injuries. 2017 guidelines of the ligament committee of the German Knee Society (DKG).Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018 Jan;138(1):51-61. doi: 10.1007/s00402-017-2809-5. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018. PMID: 28983841 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between Selected Screening Tests and Knee Alignment in Single-Leg Tasks among Young Football Players.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 31;19(11):6719. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116719. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35682301 Free PMC article.
-
Knee function and quality of life in adolescent soccer players with Osgood Shlatter disease history: a preliminary study.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 6;13(1):19200. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46537-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37932373 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of lateral ankle sprains on physical function, range of motion, isometric strength and balance in professional soccer players.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2024 Dec 22;10(4):e002293. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2024-002293. eCollection 2024. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2024. PMID: 39720151 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Quadriceps Angle on Health and Injury Risk in Female Athletes.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Nov 22;21(12):1547. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21121547. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39767389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of the FIFA 11+ Warm-Up Program on Knee Instability and Motor Performance in Male Youth Soccer Players.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 11;25(8):2425. doi: 10.3390/s25082425. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40285116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- More than Half the World Watched Record-Breaking 2018 World Cup Portal. [(accessed on 16 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.fifa.com/worldcup/news/more-than-half-the-world-watched-reco....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

