Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Episcleritis and Scleritis: An Update on Treatment Perspectives
- PMID: 34068884
- PMCID: PMC8156434
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10102118
Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Episcleritis and Scleritis: An Update on Treatment Perspectives
Abstract
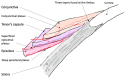
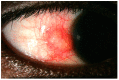
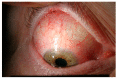
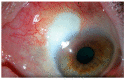
Episcleritis and scleritis are the most common ocular inflammatory manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) accounts for 8% to 15% of the cases of scleritis, and 2% of patients with RA will develop scleritis. These patients are more likely to present with diffuse or necrotizing forms of scleritis and have an increased risk of ocular complications and refractory scleral inflammation. In this review we provide an overview of diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis-associated episcleritis and scleritis with a focus on recent treatment perspectives. Episcleritis is usually benign and treated with oral non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or topical steroids. Treatment of scleritis will classically include oral NSAIDs and steroids but may require disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). In refractory cases, treatment with anti TNF biologic agents (infliximab, and adalimumab) is now recommended. Evidence suggests that rituximab may be an effective option, and further studies are needed to investigate the potential role of gevokizumab, tocilizumab, abatacept, tofacitinib, or ACTH gel. A close cooperation is needed between the rheumatology or internal medicine specialist and the ophthalmologist, especially when scleritis may be the first indicator of an underlying rheumatoid vasculitis.
Keywords: biologics; episcleritis; ocular inflammation; prognosis; rheumatoid arthritis; scleritis; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

