Daily Lifestyle and Inflammatory Skin Diseases
- PMID: 34069063
- PMCID: PMC8156947
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105204
Daily Lifestyle and Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Abstract
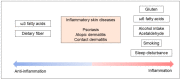
Throughout life, it is necessary to adapt to the Earth's environment in order to survive. A typical example of this is that the daily Earth cycle is different from the circadian rhythm in human beings; however, the ability to adapt to the Earth cycle has contributed to the development of human evolution. In addition, humans can consume and digest Earth-derived foods and use luxury materials for nutrition and enrichment of their lives, as an adaptation to the Earth's environment. Recent studies have shown that daily lifestyles are closely related to human health; however, less attention has been paid to the fact that obesity due to excessive energy intake, smoking, and alcohol consumption contributes to the development of inflammatory skin diseases. Gluten or wheat protein, smoking and alcohol, sleep disturbance, and obesity drive the helper T (Th)1/Th2/Th17 immune response, whereas dietary fiber and omega-3 fatty acids negatively regulate inflammatory cytokine production. In this review, we have focused on daily lifestyles and the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory skin diseases.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; contact dermatitis; daily lifestyle; psoriasis; skin inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical