An Overview of the Chemical Characteristics, Bioactivity and Achievements Regarding the Therapeutic Usage of Acetogenins from Annona cherimola Mill
- PMID: 34069113
- PMCID: PMC8155978
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26102926
An Overview of the Chemical Characteristics, Bioactivity and Achievements Regarding the Therapeutic Usage of Acetogenins from Annona cherimola Mill
Abstract
Annona cherimola Mill., or the custard apple, is one of the species belonging to the Annonaceae family, is widely used in traditional medicine, and has been reported to be a valuable source of bioactive compounds. A unique class of secondary metabolites derived from this family are Annonaceous acetogenins, lipophilic polyketides considered to be amongst the most potent antitumor compounds. This review provides an overview of the chemical diversity, isolation procedures, bioactivity, modes of application and synthetic derivatives of acetogenins from A. cherimola Mill.
Keywords: Annona cherimola; acetogenin drug delivery; acetogenin encapsulation; acetogenin formulation; acetogenins; bioactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
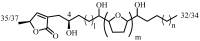





References
-
- Jamkhande P.G., Ajgunde B.R., Jadge D.R. Annona cherimola Mill. (Custard apple): A review on its plant profile, nutritional values, traditional claims and ethnomedicinal properties. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2017;17:189–201. doi: 10.1007/s13596-017-0263-0. - DOI
-
- Popenoe W. The native home of the Cherimoya. J. Hered. 1921;12:228–239. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a102116. - DOI
-
- Anaya-Esparza L.M., Ramírez-Marez M.V., Montalvo-González E., Sánchez-Burgos J.A. Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemicals. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; Chichester, UK: 2017. Cherimoya (Annona cherimola Mill.) pp. 993–1002.
-
- García-Salas P., Verardo V., Gori A., Caboni M.F., Segura-Carretero A., Fernández-Gutiérrez A. Determination of lipid composition of the two principal cherimoya cultivars grown in Andalusian Region. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016;65:390–397. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.08.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

