Propolis Extract and Its Bioactive Compounds-From Traditional to Modern Extraction Technologies
- PMID: 34069165
- PMCID: PMC8156449
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26102930
Propolis Extract and Its Bioactive Compounds-From Traditional to Modern Extraction Technologies
Abstract
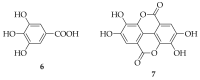
Propolis is a honeybee product known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antimicrobial effects. It is rich in bioactive molecules whose content varies depending on the botanical and geographical origin of propolis. These bioactive molecules have been studied individually and as a part of propolis extracts, as they can be used as representative markers for propolis standardization. Here, we compare the pharmacological effects of representative polyphenols and whole propolis extracts. Based on the literature data, polyphenols and extracts act by suppressing similar targets, from pro-inflammatory TNF/NF-κB to the pro-proliferative MAPK/ERK pathway. In addition, they activate similar antioxidant mechanisms of action, like Nrf2-ARE intracellular antioxidant pathway, and they all have antimicrobial activity. These similarities do not imply that we should attribute the action of propolis solely to the most representative compounds. Moreover, its pharmacological effects will depend on the efficacy of these compounds' extraction. Thus, we also give an overview of different propolis extraction technologies, from traditional to modern ones, which are environmentally friendlier. These technologies belong to an open research area that needs further effective solutions in terms of well-standardized liquid and solid extracts, which would be reliable in their pharmacological effects, environmentally friendly, and sustainable for production.
Keywords: extraction; polyphenols; propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors B.R. and S.R. are affiliated with Hedera, specializing in honeybee products since 1989. The authors J.Š. and B.R. are the co-owners of the company Apiotix Technologies, an R&D pharmaceutical company with a focus on natural extracts. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Rufatto L.C., Luchtenberg P., Garcia C., Thomassigny C., Bouttier S., Henriques J.A.P., Roesch-Ely M., Dumas F., Moura S. Brazilian red propolis: Chemical composition and antibacterial activity determined using bioguided fractionation. Microbiol. Res. 2018;214:74–82. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.05.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Do Nascimento T.G., dos Santos Arruda R.E., da Cruz Almeida E.T., dos Santos Oliveira J.M., Basílio-Júnior I.D., de Moraes Porto I.C.C., Sabino A.R., Tonholo J., Gray A., Ebel R.E., et al. Comprehensive multivariate correlations between climatic effect, metabolite-profile, antioxidant capacity and antibacterial activity of Brazilian red propolis metabolites during seasonal study. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:18293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54591-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

