Gene-Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy by Dendrimer-Like Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles against Tumor Cells
- PMID: 34069171
- PMCID: PMC8156333
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11051298
Gene-Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy by Dendrimer-Like Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles against Tumor Cells
Abstract
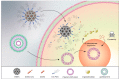
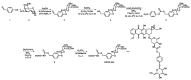
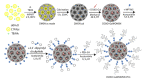
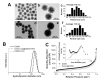
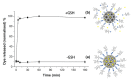
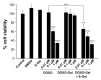
We report herein a gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (GDEPT) system using gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) in an attempt to combine the reduction of side effects characteristic of GDEPT with improved pharmacokinetics promoted by gated MSNs. The system consists of the transfection of cancer cells with a plasmid controlled by the cytomegalovirus promoter, which promotes β-galactosidase (β-gal) expression from the bacterial gene lacZ (CMV-lacZ). Moreover, dendrimer-like mesoporous silica nanoparticles (DMSNs) are loaded with the prodrug doxorubicin modified with a galactose unit through a self-immolative group (DOXO-Gal) and modified with a disulfide-containing polyethyleneglycol gatekeeper. Once in tumor cells, the reducing environment induces disulfide bond rupture in the gatekeeper with the subsequent DOXO-Gal delivery, which is enzymatically converted by β-gal into the cytotoxic doxorubicin drug, causing cell death. The combined treatment of the pair enzyme/DMSNs-prodrug are more effective in killing cells than the free prodrug DOXO-Gal alone in cells transfected with β-gal.
Keywords: DMSNs; GDEPT; drug delivery; tumor treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enzyme-induced and tumor-targeted drug delivery system based on multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 May 6;7(17):9078-87. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b00752. Epub 2015 Apr 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 25893819
-
A redox-responsive strategy using mesoporous silica nanoparticles for co-delivery of siRNA and doxorubicin.J Mater Chem B. 2017 Sep 7;5(33):6908-6919. doi: 10.1039/c7tb00613f. Epub 2017 Aug 9. J Mater Chem B. 2017. PMID: 32264340
-
Hyaluronic acid-modified mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 30;14:5785-5797. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S213974. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31440047 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome P450 gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (GDEPT) for cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2002;8(15):1405-16. doi: 10.2174/1381612023394566. Curr Pharm Des. 2002. PMID: 12052216 Review.
-
The choice of prodrugs for gene directed enzyme prodrug therapy of cancer.Gene Ther. 1995 Dec;2(10):702-9. Gene Ther. 1995. PMID: 8750009 Review.
Cited by
-
Dendrimers as Non-Viral Vectors in Gene-Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy.Molecules. 2021 Oct 1;26(19):5976. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195976. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles for Bio-Medical Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Apr 2;12(7):1189. doi: 10.3390/nano12071189. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407307 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 7;11:787780. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.787780. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34950591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Using the Sol-Gel Approach: Adjusting Architecture and Composition for Novel Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 May 21;14(11):903. doi: 10.3390/nano14110903. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38869528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

