Horse Placental Extract Enhances Neurogenesis in the Presence of Amyloid β
- PMID: 34069207
- PMCID: PMC8157028
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13051672
Horse Placental Extract Enhances Neurogenesis in the Presence of Amyloid β
Abstract
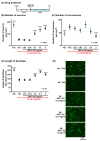
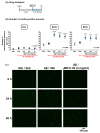
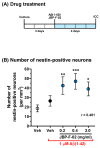
Human placental extract and animal-derived placental extracts from pigs and horses host a wide range of biological activities. Several placental products are used as medicines, cosmetics, and healthcare substances worldwide. However, the use of placental extracts for neuronal functioning is currently not established because the number of relevant studies is limited. A few previous reports suggested the neuroprotective effect and dendrite genesis effect of placental extract. However, no studies have reported on neurogenesis in placental extracts. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the effects of horse placental extract on neurogenesis, and we examined the protective effect of the extract on the onset of memory disorder. A horse placental extract, JBP-F-02, was used in this study. JBP-F-02 treatment dose-dependently increased the number of neural stem cells and dendrite length under Aβ treatment in primary cultured cortical cells. The oral administration of JBP-F-02 to a 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease at a young age significantly prevented the onset of memory dysfunction. This study suggests that the extract has the potential to prevent dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; dendrite; horse placental extract; memory recovery; neurogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
A.T. and E.H. are employees of Japan Bio Products.
Figures

References
-
- Takuma K., Mizoguchi H., Funatsu Y., Kitahara Y., Ibi D., Kamei H., Matsuda T., Koike K., Inoue M., Nagai T., et al. Placental Extract Improves Hippocampal Neuronal Loss and Fear Memory Impairment Resulting from Chronic Restraint Stress in Ovariectomized Mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012;120:89–97. doi: 10.1254/jphs.12115FP. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kogure C., Tohda C. Human Placenta Extract Ameliorates Memory Dysfunction and Dendritic Atrophy in a 5XFAD Mouse Model of A Lzheimer’s Disease. Tradit. Kamp. Med. 2017;4:94–104. doi: 10.1002/tkm2.1075. - DOI
-
- Oakley H., Cole S.L., Logan S., Maus E., Shao P., Craft J., Guillozet-Bongaarts A., Ohno M., Disterhoft J., Van Eldik L., et al. Intraneuronal Beta-Amyloid Aggregates, Neurodegeneration, and Neuron Loss in Transgenic Mice with Five Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Mutations: Potential Factors in Amyloid Plaque Formation. J. Neurosci. 2006;26:10129–10140. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1202-06.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

