Deletion of the PA4427-PA4431 Operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Increased Antibiotics Resistance and Reduced Virulence and Pathogenicity by Affecting Quorum Sensing and Iron Uptake
- PMID: 34069209
- PMCID: PMC8156433
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9051065
Deletion of the PA4427-PA4431 Operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Increased Antibiotics Resistance and Reduced Virulence and Pathogenicity by Affecting Quorum Sensing and Iron Uptake
Abstract
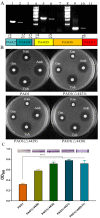
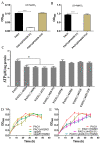
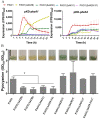
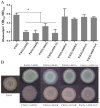
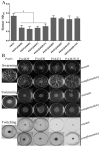
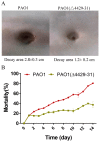
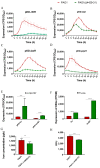
The respiratory chain is very important for bacterial survival and pathogenicity, yet the roles of the respiratory chain in P. aeruginosa remain to be fully elucidated. Here, we not only proved experimentally that the operon PA4427-PA4431 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 encodes respiratory chain complex III (cytobc1), but also found that it played important roles in virulence and pathogenicity. PA4429-31 deletion reduced the production of the virulence factors, including pyocyanin, rhamnolipids, elastase, and extracellular polysaccharides, and it resulted in a remarkable decrease in pathogenicity, as demonstrated in the cabbage and Drosophila melanogaster infection models. Furthermore, RNA-seq analysis showed that PA4429-31 deletion affected the expression levels of the genes related to quorum-sensing systems and the transport of iron ions, and the iron content was also reduced in the mutant strain. Taken together, we comprehensively illustrated the function of the operon PA4427-31 and its application potential as a treatment target in P. aeruginosa infection.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; cytochrome bc1 (cytbc1); iron transport; quorum-sensing systems; respiratory chain; virulence and pathogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium Selenite Enhances Antibiotics Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Deceases Its Pathogenicity by Inducing Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting Quorum Sensing System.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;10(12):1873. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121873. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34942975 Free PMC article.
-
Endolichenic fungus, Aspergillus quandricinctus of Usnea longissima inhibits quorum sensing and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Microb Pathog. 2020 Mar;140:103933. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103933. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 31862392
-
Proteomic analysis reveals modulation of iron homeostasis and oxidative stress response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by curcumin inhibiting quorum sensing regulated virulence factors and biofilm production.J Proteomics. 2016 Aug 11;145:112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.04.019. Epub 2016 Apr 19. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27108548
-
Interference with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Virulence by the Mycobacterial Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Dioxygenase AqdC in Combination with the N-Acylhomoserine Lactone Lactonase QsdA.Infect Immun. 2019 Sep 19;87(10):e00278-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00278-19. Print 2019 Oct. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31308081 Free PMC article.
-
The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan;69(1):25-34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001116. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31794380 Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila melanogaster as an organism model for studying cystic fibrosis and its major associated microbial infections.Infect Immun. 2023 Nov 16;91(11):e0024023. doi: 10.1128/iai.00240-23. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 37847031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

