Subcellular Alterations Induced by Cyanotoxins in Vascular Plants-A Review
- PMID: 34069255
- PMCID: PMC8157112
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10050984
Subcellular Alterations Induced by Cyanotoxins in Vascular Plants-A Review
Abstract
Phytotoxicity of cyanobacterial toxins has been confirmed at the subcellular level with consequences on whole plant physiological parameters and thus growth and productivity. Most of the data are available for two groups of these toxins: microcystins (MCs) and cylindrospermopsins (CYNs). Thus, in this review we present a timely survey of subcellular cyanotoxin effects with the main focus on these two cyanotoxins. We provide comparative insights into how peculiar plant cellular structures are affected. We review structural changes and their physiological consequences induced in the plastid system, peculiar plant cytoskeletal organization and chromatin structure, the plant cell wall, the vacuolar system, and in general, endomembrane structures. The cyanotoxins have characteristic dose-and plant genotype-dependent effects on all these structures. Alterations in chloroplast structure will influence the efficiency of photosynthesis and thus plant productivity. Changing of cell wall composition, disruption of the vacuolar membrane (tonoplast) and cytoskeleton, and alterations of chromatin structure (including DNA strand breaks) can ultimately lead to cell death. Finally, we present an integrated view of subcellular alterations. Knowledge on these changes will certainly contribute to a better understanding of cyanotoxin-plant interactions.
Keywords: cell death; cell wall; chromatin; cyanotoxin; cylindrospermopsin; cytoskeleton; microcystin; plastid; vacuole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

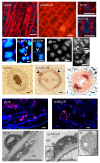
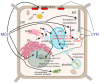
Similar articles
-
Effects of microcystin-LR and cylindrospermopsin on plant-soil systems: A review of their relevance for agricultural plant quality and public health.Environ Res. 2017 Feb;153:191-204. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.09.015. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Environ Res. 2017. PMID: 27702441 Review.
-
Microcystin-LR and cylindrospermopsin induced alterations in chromatin organization of plant cells.Mar Drugs. 2013 Sep 30;11(10):3689-717. doi: 10.3390/md11103689. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24084787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative study of cyanotoxins affecting cytoskeletal and chromatin structures in CHO-K1 cells.Toxicol In Vitro. 2009 Jun;23(4):710-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Toxicol In Vitro. 2009. PMID: 19250963
-
Cyanotoxins uptake and accumulation in crops: Phytotoxicity and implications on human health.Toxicon. 2022 May;211:21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Toxicon. 2022. PMID: 35288171 Review.
-
Beyond Microcystins: Cyanobacterial Extracts Induce Cytoskeletal Alterations in Rice Root Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 17;21(24):9649. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249649. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33348912 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate on the uptake of microcystins by Brassica oleracea and Solanum tuberosum.F1000Res. 2024 Jan 26;11:1166. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.125540.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38510265 Free PMC article.
-
Allelopathic Potential of the Cyanotoxins Microcystin-LR and Cylindrospermopsin on Green Algae.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 22;12(6):1403. doi: 10.3390/plants12061403. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36987092 Free PMC article.
-
Algicidal Activity and Microcystin-LR Destruction by a Novel Strain Penicillium sp. GF3 Isolated from the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea).Toxins (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;15(10):607. doi: 10.3390/toxins15100607. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37888639 Free PMC article.
-
Microcystin-LR, a Cyanobacterial Toxin, Induces DNA Strand Breaks Correlated with Changes in Specific Nuclease and Protease Activities in White Mustard (Sinapis alba) Seedlings.Plants (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;10(10):2045. doi: 10.3390/plants10102045. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685854 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of secondary bacterial metabolites on photosynthesis in microalgae cells.Biophys Rev. 2022 Aug 8;14(4):843-856. doi: 10.1007/s12551-022-00981-3. eCollection 2022 Aug. Biophys Rev. 2022. PMID: 36124259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Whitton B.A., Potts M. Introduction to the Cyanobacteria. In: Whitton B.A., editor. Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2012. pp. 1–13.
-
- Padisák J., Vasas G., Borics G. Phycogeography of freshwater phytoplankton: Traditional knowledge and new molecular tools. Hydrobiologia. 2016;764:3–27. doi: 10.1007/s10750-015-2259-4. - DOI
-
- Meriluoto J., Spoof L., Codd G.A. Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis. John Wiley Sons; Chichester, UK: 2017.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

