Recent Update on the Molecular Mechanisms of Gonadal Steroids Action in Adipose Tissue
- PMID: 34069293
- PMCID: PMC8157194
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105226
Recent Update on the Molecular Mechanisms of Gonadal Steroids Action in Adipose Tissue
Abstract
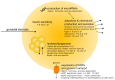
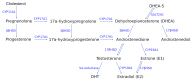
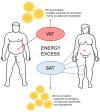
The gonadal steroids, including androgens, estrogens and progestogens, are involved in the control of body fat distribution in humans. Nevertheless, not only the size and localization of the fat depots depend on the sex steroids levels, but they can also highly affect the functioning of adipose tissue. Namely, the gonadocorticoids can directly influence insulin signaling, lipid metabolism, fatty acid uptake and adipokine production. They may also alter energy balance and glucose homeostasis in adipocytes in an indirect way, e.g., by changing the expression level of aquaglyceroporins. This work presents the recent advances in understanding the molecular mechanism of how the gonadal steroids influence the functioning of adipose tissue leading to a set of detrimental metabolic consequences. Special attention is given here to highlighting the sexual dimorphism of adipocyte functioning in terms of health and disease. Particularly, we discuss the molecular background of metabolic disturbances occurring in consequence of hormonal imbalance which is characteristic of some common endocrinopathies such as the polycystic ovary syndrome. From this perspective, we highlight the potential drug targets and the active substances which can be used in personalized sex-specific management of metabolic diseases, in accord with the patient's hormonal status.
Keywords: adipokines; adipose tissue; aquaporins; insulin sensitivity; lipid metabolism; metabolic disorders; microRNA; microRNA-oriented therapy; polycystic ovary syndrome; sex hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Klaus S. Adipose Tissue. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

