Noscapine Acts as a Protease Inhibitor of In Vitro Elastase-Induced Collagen Deposition in Equine Endometrium
- PMID: 34069423
- PMCID: PMC8159119
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105333
Noscapine Acts as a Protease Inhibitor of In Vitro Elastase-Induced Collagen Deposition in Equine Endometrium
Abstract
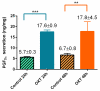
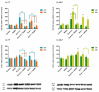
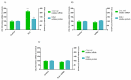
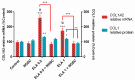
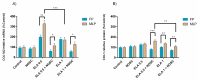
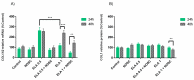
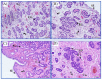
Endometrosis is a reproductive pathology that is responsible for mare infertility. Our recent studies have focused on the involvement of neutrophil extracellular traps enzymes, such as elastase (ELA), in the development of equine endometrosis. Noscapine (NOSC) is an alkaloid derived from poppy opium with anticough, antistroke, anticancer, and antifibrotic properties. The present work investigates the putative inhibitory in vitro effect of NOSC on collagen type I alpha 2 chain (COL1A2) mRNA and COL1 protein relative abundance induced by ELA in endometrial explants of mares in the follicular or mid-luteal phases at 24 or 48 h of treatment. The COL1A2 mRNA was evaluated by qPCR and COL1 protein relative abundance by Western blot. In equine endometrial explants, ELA increased COL 1 expression, while NOSC inhibited it at both estrous cycle phases and treatment times. These findings contribute to the future development of new endometrosis treatment approaches. Noscapine could be a drug capable of preventing collagen synthesis in mare's endometrium and facilitate the therapeutic approach.
Keywords: collagen; elastase; endometrosis; equine; fibrosis; inhibition; noscapine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kenney R.M., Doig P.A. Equine endometrial biopsy. In: Morrow D.A., editor. Current Therapy in Theriogenology 2: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Reproductive Diseases in Small and Large Animals. 2nd ed. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 1986. pp. 723–729.
-
- Kenney R.M. The aetiology, diagnosis, and classification of chronic degenerative endometritis. In: Hughes J.P., editor. Workshop on Equine Endometritis. Volume 125. Newmarket Press; New York, NY, USA: 1992. p. 186.
-
- Katkiewicz M., Witkowski M., Zajac S. Endometrial biopsy of mares: Visualization of healthy and diseased structure. Med. Weter. 2007;63:463–466.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

