Role of Glycans on Key Cell Surface Receptors That Regulate Cell Proliferation and Cell Death
- PMID: 34069424
- PMCID: PMC8159107
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10051252
Role of Glycans on Key Cell Surface Receptors That Regulate Cell Proliferation and Cell Death
Abstract
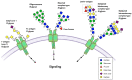
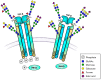
Cells undergo proliferation and apoptosis, migration and differentiation via a number of cell surface receptors, most of which are heavily glycosylated. This review discusses receptor glycosylation and the known roles of glycans on the functions of receptors expressed in diverse cell types. We included growth factor receptors that have an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, growth factor receptors that have a serine/threonine kinase domain, and cell-death-inducing receptors. N- and O-glycans have a wide range of functions including roles in receptor conformation, ligand binding, oligomerization, and activation of signaling cascades. A better understanding of these functions will enable control of cell survival and cell death in diseases such as cancer and in immune responses.
Keywords: N-glycans; O-glycans; TGFR; receptors; signaling; tyrosine kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wajant H. Death receptors. Essays Biochem. 2003;39:53–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

