Prognostic Role of Immune Checkpoint Regulators in Cholangiocarcinoma: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 34069452
- PMCID: PMC8159105
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10102191
Prognostic Role of Immune Checkpoint Regulators in Cholangiocarcinoma: A Pilot Study
Abstract
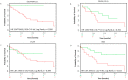
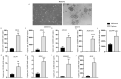
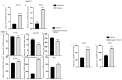
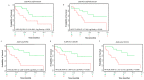
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a hepatobiliary malignancy associated with steadily increasing incidence and poor prognosis. Ongoing clinical trials are assessing the effectiveness and safety of a few immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in CCA patients. However, these ICI treatments as monotherapies may be effective for a proportion of patients with CCA. The prevalence and distribution of other immune checkpoints (ICs) in CCA remain unclear. In this pilot study, we screened databases of CCA patients for the expression of 19 ICs and assessed the prognostic significance of these ICs in CCA patients. Notably, expression of immune modulator IDO1 and PD-L1 were linked with poor overall survival, while FASLG and NT5E were related to both worse overall survival and progression-free survival. We also identified immune modulators IDO1, FASLG, CD80, HAVCR2, NT5E, CTLA-4, LGALS9, VTCN1 and TNFRSF14 that synergized with PD-L1 and correlated with worse patient outcomes. In vitro studies revealed that the expression of ICs was closely linked with aggressive CCA subpopulations, such as cancer stem cells and cells undergoing TGF-β and TNF-α-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. These findings suggest that the aforementioned IC molecules may serve as potential prognostic biomarkers and drug targets in CCA patients, leading to lasting and durable treatment outcomes.
Keywords: CD73; EMT; Galectin-9; IDO1; PD-L1; cancer stem cells; cholangiocarcinoma; immune checkpoints.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

