Exposure to RF-EMF Alters Postsynaptic Structure and Hinders Neurite Outgrowth in Developing Hippocampal Neurons of Early Postnatal Mice
- PMID: 34069478
- PMCID: PMC8159076
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105340
Exposure to RF-EMF Alters Postsynaptic Structure and Hinders Neurite Outgrowth in Developing Hippocampal Neurons of Early Postnatal Mice
Abstract
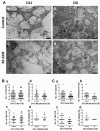
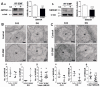
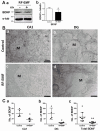
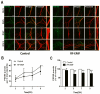
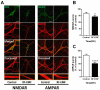
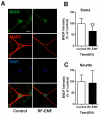
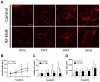
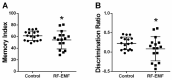
Exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMFs) has increased rapidly in children, but information on the effects of RF-EMF exposure to the central nervous system in children is limited. In this study, pups and dams were exposed to whole-body RF-EMF at 4.0 W/kg specific absorption rate (SAR) for 5 h per day for 4 weeks (from postnatal day (P) 1 to P28). The effects of RF-EMF exposure on neurons were evaluated by using both pups' hippocampus and primary cultured hippocampal neurons. The total number of dendritic spines showed statistically significant decreases in the dentate gyrus (DG) but was not altered in the cornu ammonis (CA1) in hippocampal neurons. In particular, the number of mushroom-type dendritic spines showed statistically significant decreases in the CA1 and DG. The expression of glutamate receptors was decreased in mushroom-type dendritic spines in the CA1 and DG of hippocampal neurons following RF-EMF exposure. The expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the CA1 and DG was significantly lower statistically in RF-EMF-exposed mice. The number of post-synaptic density protein 95 (PSD95) puncta gradually increased over time but was significantly decreased statistically at days in vitro (DIV) 5, 7, and 9 following RF-EMF exposure. Decreased BDNF expression was restricted to the soma and was not observed in neurites of hippocampal neurons following RF-EMF exposure. The length of neurite outgrowth and number of branches showed statistically significant decreases, but no changes in the soma size of hippocampal neurons were observed. Further, the memory index showed statistically significant decreases in RF-EMF-exposed mice, suggesting that decreased synaptic density following RF-EMF exposure at early developmental stages may affect memory function. Collectively, these data suggest that hindered neuronal outgrowth following RF-EMF exposure may decrease overall synaptic density during early neurite development of hippocampal neurons.
Keywords: RF-EMF; dendritic spine; glutamate receptor; hippocampus; neurite outgrowth; neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exposure to Radiofrequency Induces Synaptic Dysfunction in Cortical Neurons Causing Learning and Memory Alteration in Early Postnatal Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 6;25(16):8589. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168589. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201275 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the excitability of primary hippocampal neurons following exposure to 3.0 GHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 3;12(1):3506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06914-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35241689 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to 1800 MHz radiofrequency radiation impairs neurite outgrowth of embryonic neural stem cells.Sci Rep. 2014 May 29;4:5103. doi: 10.1038/srep05103. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24869783 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field (RF-EMF) exposure on pregnancy and birth outcomes: A systematic review of experimental studies on non-human mammals.Environ Int. 2023 Oct;180:108178. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2023.108178. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Environ Int. 2023. PMID: 37729852
-
Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field (RF-EMF) exposure on male fertility: A systematic review of experimental studies on non-human mammals and human sperm in vitro.Environ Int. 2024 Mar;185:108509. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108509. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 38492496
Cited by
-
1,800 MHz Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Irradiation Impairs Neurite Outgrowth With a Decrease in Rap1-GTP in Primary Mouse Hippocampal Neurons and Neuro2a Cells.Front Public Health. 2021 Nov 22;9:771508. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.771508. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34881219 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile Phone Radiation Deflects Brain Energy Homeostasis and Prompts Human Food Ingestion.Nutrients. 2022 Jan 14;14(2):339. doi: 10.3390/nu14020339. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35057520 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Synapto-protective effect of lithium on HIV-1 Tat-induced synapse loss in rat hippocampal cultures.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2021 Dec 27;26(1):1-9. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2021.2018044. eCollection 2022. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 35308128 Free PMC article.
-
Impressions of the chronic 900-MHz electromagnetic field in the prenatal period on Purkinje cells in male rat pup cerebella: is it worth mentioning?Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2022 Nov 21;68(10):1383-1388. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20220893. eCollection 2022. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2022. PMID: 36417640 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation improves the synapses and cognitive function and ameliorates epileptic seizure by inhibiting downregulation of Nlgn3.Cell Biosci. 2023 Jan 12;13(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00949-6. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36635704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birks L.E., Struchen B., Eeftens M., van Wel L., Huss A., Gajšek P., Kheifets L., Gallastegi M., Dalmau-Bueno A., Estarlich M., et al. Spatial and temporal variability of personal environmental exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields in children in Europe. Environ. Int. 2018;117:204–214. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.04.026. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

