Effectiveness of 0.66% Povidone-Iodine Eye Drops on Ocular Surface Flora before Cataract Surgery: A Nationwide Microbiological Study
- PMID: 34069600
- PMCID: PMC8160713
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10102198
Effectiveness of 0.66% Povidone-Iodine Eye Drops on Ocular Surface Flora before Cataract Surgery: A Nationwide Microbiological Study
Abstract
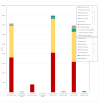
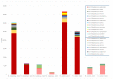
A multicenter, nonrandomized, prospective, controlled study was conducted to evaluate, as perioperative prophylactic treatment, the anti-infective effectiveness of 0.66% povidone-iodine eye drops (IODIM®) against the bacterial flora of the conjunctival surface of patients who undergo cataract surgery. Eye drops containing 0.66% povidone-iodine were applied to the eye undergoing cataract surgery; the untreated contralateral eye was used as control. One hundred and twenty patients set to receive unilateral cataract surgery were enrolled in 5 Italian Ophthalmology Centers and pretreated for three days with 0.66% povidone-iodine eye drops. The contralateral eye, used as control, was left untreated. Conjunctival swabs of both eyes were collected at the baseline visit and after three days of treatment, just before the cataract surgery. A qualitative and quantitative microbiological analysis of bacterial presence was evaluated by means of bacterial culture, followed by identification. Methicillin resistance determination was also performed on staphylococci isolates. Bacterial load before and after treatment of the eye candidate for cataract surgery was evaluated and compared to the untreated eye. A reduction or no regrowth on the culture media of the bacterial load was observed in 100% of the study subjects. A great heterogenicity of bacterial species was found. The 0.66% povidone-iodine eye drops, used for three days prior to cataract surgery, were effective in reducing the conjunctival bacterial load. The 0.66% povidone-iodine eye drops (IODIM®) might represent a valid perioperative prophylactic antiseptic adjuvant treatment to protect the ocular surface from microbial contamination in preparation of the surgical procedure.
Keywords: antiseptic prophylactic treatment; cataract; endophthalmitis; ocular surgery; povidone iodine.
Conflict of interest statement
Rosario Musumeci received research funding from Medivis srl (Catania, Italy) in the past years, but it was not related to this study. No conflicting relationship exists for any other author. The funders of Rosario Musumeci had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

