Antiplatelet Activity of Coumarins: In Vitro Assays on COX-1
- PMID: 34069658
- PMCID: PMC8161015
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26103036
Antiplatelet Activity of Coumarins: In Vitro Assays on COX-1
Abstract
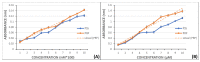
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in developed countries. Therefore, there is an increasing interest in developing new potent and safe antiplatelet agents. Coumarins are a family of polyphenolic compounds with several pharmacological activities, including platelet aggregation inhibition. However, their antiplatelet mechanism of action needs to be further elucidated. The aim of this study is to provide insight into the biochemical mechanisms involved in this activity, as well as to establish a structure-activity relationship for these compounds. With this purpose, the antiplatelet aggregation activities of coumarin, esculetin and esculin were determined in vitro in human whole blood and platelet-rich plasma, to set the potential interference with the arachidonic acid cascade. Here, the platelet COX activity was evaluated from 0.75 mM to 6.5 mM concentration by measuring the levels of metabolites derived from its activity (MDA and TXB2), together with colorimetric assays performed with the pure recombinant enzyme. Our results evidenced that the coumarin aglycones present the greatest antiplatelet activity at 5 mM and 6.5 mM on aggregometry experiments and inhibiting MDA levels.
Keywords: COX; antiplatelet activity; coumarin; esculetin; esculin; impedance aggregometry; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

