Macrofungi as a Nutraceutical Source: Promising Bioactive Compounds and Market Value
- PMID: 34069721
- PMCID: PMC8161071
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7050397
Macrofungi as a Nutraceutical Source: Promising Bioactive Compounds and Market Value
Abstract
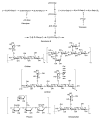
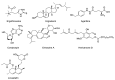
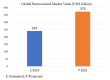
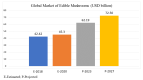
Macrofungi production and economic value have been increasing globally. The demand for macrofungi has expanded rapidly owing to their popularity among consumers, pleasant taste, and unique flavors. The presence of high quality proteins, polysaccharides, unsaturated fatty acids, minerals, triterpene sterols, and secondary metabolites makes macrofungi an important commodity. Macrofungi are well known for their ability to protect from or cure various health problems, such as immunodeficiency, cancer, inflammation, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity. Many studies have demonstrated their medicinal properties, supported by both in vivo and in vitro experimental studies, as well as clinical trials. Numerous bioactive compounds isolated from mushrooms, such as polysaccharides, proteins, fats, phenolic compounds, and vitamins, possess strong bioactivities. Consequently, they can be considered as an important source of nutraceuticals. Numerous edible mushrooms have been studied for their bioactivities, but only a few species have made it to the market. Many species remain to be explored. The converging trends and popularity of eastern herbal medicines, natural/organic food product preference, gut-healthy products, and positive outlook towards sports nutrition are supporting the growth in the medicinal mushroom market. The consumption of medicinal mushrooms as functional food or dietary supplement is expected to markedly increase in the future. The global medicinal mushroom market size is projected to increase by USD 13.88 billion from 2018 to 2022. The global market values of promising bioactive compounds, such as lentinan and lovastatin, are also expected to rise. With such a market growth, mushroom nutraceuticals hold to be very promising in the years to come.
Keywords: bioactivities; macrofungi; market value; medicinal properties; nutraceuticals; nutrients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Edible mushrooms as meat analogues: A comprehensive review of nutritional, therapeutic, and market potential.Food Res Int. 2025 Aug;214:116632. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116632. Epub 2025 May 15. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40467220 Review.
-
Nutraceuticals, a Bridge Between Past and Future: Focus on Mushrooms Biological Activities and Myco-Chemistry.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(3):320-335. doi: 10.2174/1389557522666220622104845. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35733302 Review.
-
Medicinal mushroom: boon for therapeutic applications.3 Biotech. 2018 Aug;8(8):334. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1358-0. Epub 2018 Jul 23. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30073119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Health-promoting Potential of Edible Mushroom Proteins.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(11):804-823. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221223103756. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 36567303 Review.
-
Macrofungi: A review of cultivation strategies, bioactivity, and application of mushrooms.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020 Sep;19(5):2333-2356. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12602. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020. PMID: 33336985 Review.
Cited by
-
Community composition and trophic mode diversity of fungi associated with fruiting body of medicinal Sanghuangporus vaninii.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Oct 19;22(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02663-2. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36261787 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable Environmental Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Practices: Co-Pyrolysis of Food Waste and Discarded Meal Boxes.Foods. 2022 Nov 28;11(23):3840. doi: 10.3390/foods11233840. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36496648 Free PMC article.
-
The benefits of edible mushroom polysaccharides for health and their influence on gut microbiota: a review.Front Nutr. 2023 Jul 6;10:1213010. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1213010. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37485384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of nanocrystals in cancer theranostics.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Jul 10;5(16):4018-4040. doi: 10.1039/d3na00397c. eCollection 2023 Aug 8. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 37560418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Oyster Mushrooms as a Functional Food for Complementary Cancer Therapy.Foods. 2025 Jan 4;14(1):128. doi: 10.3390/foods14010128. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39796417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Willis K.J. State of the World’s Fungi 2018. [(accessed on 18 March 2021)]; Available online: https://stateoftheworldsfungi.org/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

