Platelet Receptor Activity for Predicting Survival in Patients with Intracranial Bleeding
- PMID: 34069736
- PMCID: PMC8160693
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10102205
Platelet Receptor Activity for Predicting Survival in Patients with Intracranial Bleeding
Abstract
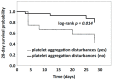
Blood coagulation disorders in patients with intracranial bleeding as a result of head injuries or ruptured aneurysms are a diagnostic and therapeutic problem and appropriate assessments are needed to limit CNS damage and to implement preventive measures. The aim of the study was to monitor changes in platelet aggregation and to assess the importance of platelet dysfunction for predicting survival. Platelet receptor function analysis was performed using the agonists arachidonic acid (ASPI), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), collagen (COL), thrombin receptor activating protein (TRAP), ristocetin (RISTO) upon admission to the ICU and on days 2, 3, and 5. On admission, the ASPI, ADP, COL, TRAP, and RISTO tests indicated there was reduced platelet aggregation, despite there being a normal platelet count. In 'Non-survivors', the platelet response to all agonists was suppressed throughout the study period, while in 'Survivors' it improved. Measuring platelet function in ICU patients with intracranial bleeding is a strong predictor related to outcome: patients with impaired platelet aggregation had a lower 28-day survival rate compared to patients with normal platelet aggregation (log-rank test p = 0.014). The results indicated that measuring platelet aggregation can be helpful in the early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of bleeding disorders.
Keywords: aneurysm; craniocerebral trauma; intracranial hemorrhages; platelet aggregation; platelet function tests; ruptured; survival rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

