Effects of Functionalization in Different Conditions and Ball Milling on the Dispersion and Thermal and Electrical Conductivity of MWCNTs in Aqueous Solution
- PMID: 34069773
- PMCID: PMC8157300
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11051323
Effects of Functionalization in Different Conditions and Ball Milling on the Dispersion and Thermal and Electrical Conductivity of MWCNTs in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
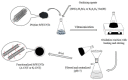
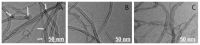
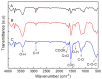
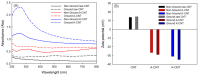
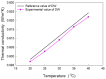
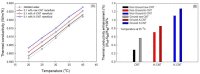
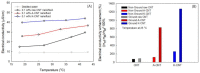
In this work, the effects of a functionalization method involving different conditions and milling processes on the dispersion and thermal and electrical conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes were studied. The surfaces of MWCNTs were modified using a mixture of sulfuric and nitric acid as an acid treatment and potassium persulfate and sodium hydroxide as an alkaline treatment to achieve more hydrophilic MWCNTs. The morphological and structural investigations were carried out using transmission electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Furthermore, the dispersion characteristics and thermal and electrical conductivity of the as-prepared water-based nanofluids were measured. As a result, the dispersion characteristics revealed that the best dispersion and stability results were obtained for alkaline-treated MWCNTs using potassium persulfate and sodium hydroxide. The thermophysical study using a thermal conductivity analyzer exhibited that the thermal conductivity of the pristine MWCNT nanofluid (0.1 wt%) was enhanced from 603.5 to 610.4 mW/m·K and the electrical conductivity of the raw MWCNT nanofluid was increased from 16.2 to 125.8 μS/cm at 25 °C after alkaline treatment and milling processes, which were performed using planetary ball milling. Regarding the overall results, the milling process and mild alkaline oxidation process are more environmentally friendly, effective, and convenient for the functionalization of CNTs, without requiring any organic solvents or strong acids.
Keywords: MWCNTs; alkaline treatment; dispersion; functionalization; thermal conductivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Moore V.C., Strano M.S., Haroz E.H., Hauge R.H., Smalley R.E., Schmidt J., Talmon Y. Individually suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes in various surfactants. Nano Lett. 2003;3:1379–1382. doi: 10.1021/nl034524j. - DOI
-
- Vaccarini L., Goze C., Henrard L., Hernandez E., Bernier P., Rubio A. Mechanical and electronic properties of carbon and boron–nitride nanotube. Carbon. 2000;38:1681–1690. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00293-6. - DOI
-
- Casas C., Li W. A review of application of carbon nanotubes for lithium ion battery anode material. J. Power Sources. 2012;208:74–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.02.013. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

