Optogenetic Approaches for the Spatiotemporal Control of Signal Transduction Pathways
- PMID: 34069904
- PMCID: PMC8157557
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105300
Optogenetic Approaches for the Spatiotemporal Control of Signal Transduction Pathways
Abstract
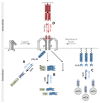
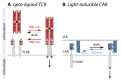
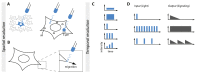
Biological signals are sensed by their respective receptors and are transduced and processed by a sophisticated intracellular signaling network leading to a signal-specific cellular response. Thereby, the response to the signal depends on the strength, the frequency, and the duration of the stimulus as well as on the subcellular signal progression. Optogenetic tools are based on genetically encoded light-sensing proteins facilitating the precise spatiotemporal control of signal transduction pathways and cell fate decisions in the absence of natural ligands. In this review, we provide an overview of optogenetic approaches connecting light-regulated protein-protein interaction or caging/uncaging events with steering the function of signaling proteins. We briefly discuss the most common optogenetic switches and their mode of action. The main part deals with the engineering and application of optogenetic tools for the control of transmembrane receptors including receptor tyrosine kinases, the T cell receptor and integrins, and their effector proteins. We also address the hallmarks of optogenetics, the spatial and temporal control of signaling events.
Keywords: control of function; optogenetics; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Optogenetic control of signaling in mammalian cells.Biotechnol J. 2015 Feb;10(2):273-83. doi: 10.1002/biot.201400077. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25216399 Review.
-
Optogenetic tools for dissecting complex intracellular signaling pathways.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 25;527(2):331-336. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.12.132. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 31948753 Review.
-
Optogenetics - Bringing light into the darkness of mammalian signal transduction.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Feb;1864(2):280-292. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 27845208 Review.
-
Regulation of endogenous transmembrane receptors through optogenetic Cry2 clustering.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 22;6:6898. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7898. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25902152 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Application of Light-Regulated Receptor Tyrosine Kinases.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2173:233-246. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0755-8_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32651922
Cited by
-
Modulatory Effect of Gut Microbiota on the Gut-Brain, Gut-Bone Axes, and the Impact of Cannabinoids.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 10;12(12):1247. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121247. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36557285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetic therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes. 2024 Jun;16(6):e13557. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13557. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38751366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetic Control of the Mitochondrial Protein Import in Mammalian Cells.Cells. 2024 Oct 9;13(19):1671. doi: 10.3390/cells13191671. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404433 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Cycle Control by Optogenetically Regulated Cell Cycle Inhibitor Protein p21.Biology (Basel). 2023 Aug 31;12(9):1194. doi: 10.3390/biology12091194. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37759593 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic perturbation of lipid droplet localization affects lipid metabolism and development in Drosophila.J Lipid Res. 2025 Aug;66(8):100848. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100848. Epub 2025 Jun 20. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 40545239 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

