Risk of Dry Eye Syndrome in Patients with Orbital Fracture: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- PMID: 34070017
- PMCID: PMC8157863
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9050605
Risk of Dry Eye Syndrome in Patients with Orbital Fracture: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
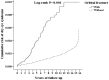
This study aimed to investigate whether orbital fracture increases the risk of dry eye syndrome (DES) and identified the profile of prognostic factors. We studied a cohort from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). Overall, 46,179 and 184,716 participants were enrolled in the study and control groups, respectively. Each patient in the case group was age- and gender-matched to four individuals without orbital fracture that served as the control group. Cox proportional hazards analysis regression was used to estimate the risks of incident DES. During the follow-up period, the case group was more likely to develop incident DES (0.17%) than the control group (0.11%) (p = 0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that the case group had a 4.917-fold increased risk of DES compared to the controls. In the stratified age group, orbital fracture had the highest impact on patients aged 18-29 years. Furthermore, patients with orbital roof fracture have a greater risk of developing DES. Regardless of whether having received surgery or not, the patients with orbital fracture have higher risks of DES. Our study demonstrated that orbital fracture increases the risk of developing subsequent DES. Early recognition by thorough examinations with raised awareness in the clinical setting could preserve visual function and prevent further complications.
Keywords: dry eye syndrome; ocular surface; orbital fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dry eye syndrome and the subsequent risk of chronic fatigue syndrome-a prospective population-based study in Taiwan.Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 17;9(55):30694-30703. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25544. eCollection 2018 Jul 17. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30093979 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence of Dry Eye Syndrome's and the Likelihood to Develop Sjögren's Syndrome in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Jul 8;12(7):7647-55. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120707647. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26184245 Free PMC article.
-
The association of dry eye syndrome and psychiatric disorders: a nationwide population-based cohort study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Mar 30;20(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01395-z. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32228638 Free PMC article.
-
Association of age-related macular degeneration on fracture risks among osteoporosis population: a nationwide population-based cohort study.BMJ Open. 2020 Sep 17;10(9):e037028. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037028. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32948557 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and morbidity in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta in Denmark.Dan Med J. 2018 Apr;65(4):B5454. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29619932 Review.
Cited by
-
A nationwide population-based study on epidemiologic characteristics and treatment patterns of dry eye disease in South Korea.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 4;15(1):28470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07228-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40759910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koenen L., Waseem M. Stat. Pearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2019. Orbital Floor (Blowout) Fracture.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources