The Pro-Oxidant Activity of Red Wine Polyphenols Induces an Adaptive Antioxidant Response in Human Erythrocytes
- PMID: 34070135
- PMCID: PMC8158335
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10050800
The Pro-Oxidant Activity of Red Wine Polyphenols Induces an Adaptive Antioxidant Response in Human Erythrocytes
Abstract
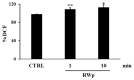
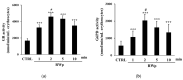
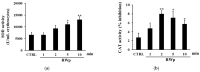
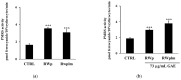
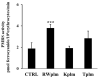
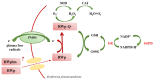
The protective effect of dealcoholized red wine on human health has been partially associated with its polyphenolic components, suggesting that the pool of polyphenols, including flavonoids and anthocyanins, can be responsible for the functional effects of this beverage. We hypothesize a new role of red wine polyphenols (RWp) in modulating the antioxidant potential of erythrocytes, protecting them against oxidative stress. We previously demonstrated that RWp activated the Plasma Membrane Redox System (PMRS), which is involved in neutralizing plasma free radicals. Here, we investigated the underlying mechanism triggered by RWp in the activation of PMRS via the involvement of GSH. Hence, treatment of human erythrocytes with RWp (73 μg/mL Gallic Acid Equivalents) increased GSH intracellular concentration, which depends upon the activation of glutathione reductase (GR) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), whose enzymatic activities increase of about 30% and 47%, respectively. Changes in the GSH pathway induced by RWp were associated with a slight but significant increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS). We conclude that the pro-oxidant effect of RWp promoted an adaptive stress response in human erythrocytes, which enhances their antioxidant defense.
Keywords: PMRS; adaptive response; antioxidant; erythrocytes; red wine polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
Author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Red wine activates plasma membrane redox system in human erythrocytes.Free Radic Res. 2016;50(5):557-69. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2016.1152629. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Free Radic Res. 2016. PMID: 26866566
-
Proteomic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to study the effects of red wine polyphenols on oxidative stress.J Food Sci Technol. 2019 Sep;56(9):4129-4138. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-03883-7. Epub 2019 Jun 28. J Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 31477984 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of red wine polyphenols on vascular smooth muscle cell function--molecular mechanism of the 'French paradox'.Mech Ageing Dev. 2002 Apr 30;123(8):1033-9. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(01)00386-4. Mech Ageing Dev. 2002. PMID: 12044952
-
Oxidative stress and protective effects of polyphenols: comparative studies in human and rodent kidney. A review.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006 Mar-Apr;142(3-4):317-327. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2005.11.002. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16380298 Review.
-
Renal damage mediated by oxidative stress: a hypothesis of protective effects of red wine.Free Radic Biol Med. 2002 Aug 1;33(3):409-22. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(02)00908-5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002. PMID: 12126763 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant/Pro-Oxidant Actions of Polyphenols From Grapevine and Wine By-Products-Base for Complementary Therapy in Ischemic Heart Diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 3;8:750508. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.750508. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34805304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red Wine and Sexual Function in Men: An Original Point of View.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 7;12(12):3883. doi: 10.3390/jcm12123883. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373577 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Silico Interaction Studies with Red Wine Polyphenols against Different Proteins from Human Serum.Molecules. 2021 Nov 5;26(21):6686. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216686. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771095 Free PMC article.
-
From Fighting Critters to Saving Lives: Polyphenols in Plant Defense and Human Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 20;22(16):8995. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168995. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin treatment enhances bioactive metabolite accumulation and reduces enzymatic browning in soybean sprouts during storage.Food Chem X. 2023 Feb 21;17:100607. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100607. eCollection 2023 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2023. PMID: 36974192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russo G.L., Siani A., Fogliano V., Geleijnse J.M., Giacco R., Giampaoli S., Iacoviello L., Kromhout D., Lionetti L., Naska A., et al. The Mediterranean diet from past to future: Key concepts from the second “Ancel Keys” International Seminar. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021;31:717–732. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.12.020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

