PPI Modulators of E6 as Potential Targeted Therapeutics for Cervical Cancer: Progress and Challenges in Targeting E6
- PMID: 34070144
- PMCID: PMC8158384
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26103004
PPI Modulators of E6 as Potential Targeted Therapeutics for Cervical Cancer: Progress and Challenges in Targeting E6
Abstract
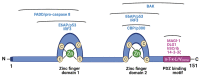
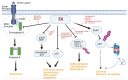
Advanced cervical cancer is primarily managed using cytotoxic therapies, despite evidence of limited efficacy and known toxicity. There is a current lack of alternative therapeutics to treat the disease more effectively. As such, there have been more research endeavors to develop targeted therapies directed at oncogenic host cellular targets over the past 4 decades, but thus far, only marginal gains in survival have been realized. The E6 oncoprotein, a protein of human papillomavirus origin that functionally inactivates various cellular antitumor proteins through protein-protein interactions (PPIs), represents an alternative target and intriguing opportunity to identify novel and potentially effective therapies to treat cervical cancer. Published research has reported a number of peptide and small-molecule modulators targeting the PPIs of E6 in various cell-based models. However, the reported compounds have rarely been well characterized in animal or human subjects. This indicates that while notable progress has been made in targeting E6, more extensive research is needed to accelerate the optimization of leads. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge and understanding of specific E6 PPI inhibition, the progress and challenges being faced, and potential approaches that can be utilized to identify novel and potent PPI inhibitors for cervical cancer treatment.
Keywords: HPV E6; cervical cancer; drug discovery; peptides; protein–protein interactions; small molecules; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential drugs against cervical cancer: zinc-ejecting inhibitors of the human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999 Jul 21;91(14):1211-20. doi: 10.1093/jnci/91.14.1211. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999. PMID: 10413422
-
A quantitative LumiFluo assay to test inhibitory compounds blocking p53 degradation induced by human papillomavirus oncoprotein E6 in living cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 16;8(1):6020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24470-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29662081 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoradiation of cervical cancer cells: targeting human papillomavirus E6 and p53 leads to either augmented or attenuated apoptosis depending on the platinum carrier ligand.Cancer Res. 2002 Dec 15;62(24):7364-71. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12499281
-
Targeting Protein-Protein Interactions in Hematologic Malignancies.Annu Rev Pathol. 2025 Jan;20(1):275-301. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-031521-033231. Annu Rev Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39854187 Review.
-
The Potential of Peptide-Based Inhibitors in Disrupting Protein-Protein Interactions for Targeted Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 28;26(7):3117. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073117. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endocytosis and Transcytosis of SARS-CoV-2 Across the Intestinal Epithelium and Other Tissue Barriers.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 7;12:636966. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636966. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34557180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACE2 : S1 RBD Interaction-Targeted Peptides and Small Molecules as Potential COVID-19 Therapeutics.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021 Nov 2;2021:1828792. doi: 10.1155/2021/1828792. eCollection 2021. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34746794 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Alpha and Beta HPV E6 Oncoproteins: Insights into Functional Distinctions and Divergent Mechanisms of Pathogenesis.Viruses. 2023 Nov 14;15(11):2253. doi: 10.3390/v15112253. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
30-hydroxygambogic acid increases the efficacy of cisplatin in an HPV+ head and neck cancer in vivo model.BMC Cancer. 2025 Aug 1;25(1):1251. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14638-3. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40745291 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting HSP70-E7 Interaction With SHetA2: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Cervical Cancer.J Med Virol. 2024 Nov;96(11):e70088. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70088. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 39588793
References
-
- Bruni L., Diaz M., Barrionuevo-Rosas L., Herrero R., Bray F., Bosch F.X., de Sanjosé S., Castellsagué X. Global estimates of human papillomavirus vaccination coverage by region and income level: A pooled analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2016;4:e453–e463. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30099-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

