Proteomic Profile of Saliva in Parkinson's Disease Patients: A Proof of Concept Study
- PMID: 34070185
- PMCID: PMC8158489
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11050661
Proteomic Profile of Saliva in Parkinson's Disease Patients: A Proof of Concept Study
Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. It affects many organs. Lewy bodies-a histopathological "hallmark" of PD-are detected in about 75% of PD submandibular gland samples. We hypothesize that saliva can be a source of biomarkers of PD. The aim of the study was to evaluate and compare the salivary proteome of PD patients and healthy controls (HC). Salivary samples from 39 subjects (24 PD patients, mean age 61.6 ± 8.2; 15 HC, mean age 60.9 ± 6.7) were collected. Saliva was collected using RNA-Pro-Sal kits. Label-free LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry was performed to characterize the proteome of the saliva. IPA analysis of upstream inhibitors was performed. A total of 530 proteins and peptides were identified. We observed lower concentrations of S100-A16, ARP2/3, and VPS4B in PD group when compared to HC. We conclude that the salivary proteome composition of PD patients is different than that of healthy controls. We observed a lower concentration of proteins involved in inflammatory processes, exosome formation, and adipose tissue formation. The variability of expression of proteins between the two groups needs to be considered.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; neurodegeneration; proteomic profile; saliva; salivary glands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
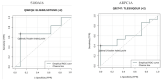
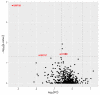
References
-
- Goldman J.G., Andrews H., Amara A., Naito A., Alcalay R.N., Shaw L.M., Taylor P., Xie T., Tuite P., Henchcliffe C. Cerebrospinal fluid, plasma, and saliva in the BioFIND study: Relationships among biomarkers and Parkinson’s disease features. Mov. Disord. 2018;33:282–288. doi: 10.1002/mds.27232. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chahine L.M., Beach T.G., Seedorff N., Caspell-Garcia C., Coffey C.S., Brumm M., Adler C.H., Serrano G.E., Linder C., Mosovsky S. Feasibility and Safety of Multicenter Tissue and Biofluid Sampling for α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease: The Systemic Synuclein Sampling Study (S4) J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2018;8:517–527. doi: 10.3233/JPD-181434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

