Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related?
- PMID: 34070400
- PMCID: PMC8228660
- DOI: 10.3390/md19060304
Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related?
Abstract
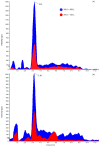
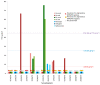
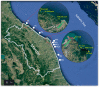
Tetrodotoxins (TTXs), potent neurotoxins, have become an increasing concern in Europe in recent decades, especially because of their presence in mollusks. The European Food Safety Authority published a Scientific Opinion setting a recommended threshold for TTX in mollusks of 44 µg equivalent kg-1 and calling all member states to contribute to an effort to gather data in order to produce a more exhaustive risk assessment. The objective of this work was to assess TTX levels in wild and farmed mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) harvested in 2018-2019 along the coastal area of the Marche region in the Central Adriatic Sea (Italy). The presence of Vibrio spp. carrying the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) and polyketide synthase (PKS) genes, which are suspected to be involved in TTX biosynthesis, was also investigated. Out of 158 mussel samples analyzed by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-MS/MS), 11 (7%) contained the toxins at detectable levels (8-26 µg kg-1) and 3 (2%) contained levels above the EFSA safety threshold (61-76 µg kg-1). Contaminated mussels were all harvested from natural beds in spring or summer. Of the 2019 samples, 70% of them contained V. alginolyticus strains with the NRPS and/or PKS genes. None of the strains containing NRPS and/or PKS genes showed detectable levels of TTXs. TTXs in mussels are not yet a threat in the Marche region nor in Europe, but further investigations are surely needed.
Keywords: Adriatic Sea; HILIC-MS/MS; NRPS gene; PKS gene; Vibrio alginolyticus; bacterial pellets; mussels; tetrodotoxins (TTXs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Hotspot of TTX Contamination in the Adriatic Sea: Study on the Origin and Causative Factors.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 22;21(1):8. doi: 10.3390/md21010008. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662181 Free PMC article.
-
First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Bivalves and Gastropods from the French Mainland Coasts.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 16;12(9):599. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090599. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32947992 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrodotoxin in live bivalve mollusks from Europe: Is it to be considered an emerging concern for food safety?Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022 Jan;21(1):719-737. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12881. Epub 2021 Dec 26. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022. PMID: 34954887
-
Shellfish and residual chemical contaminants: hazards, monitoring, and health risk assessment along French coasts.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011;213:55-111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_3. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21541848 Review.
-
Tetrodotoxin in marine bivalves and edible gastropods: A mini-review.Chemosphere. 2019 Dec;236:124404. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124404. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Chemosphere. 2019. PMID: 31545201 Review.
Cited by
-
Tetrodotoxins in French Bivalve Mollusks-Analytical Methodology, Environmental Dynamics and Screening of Bacterial Strain Collections.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 20;13(11):740. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110740. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34822524 Free PMC article.
-
An Update of Tetrodotoxins Toxicity and Risk Assessment Associated to Contaminated Seafood Consumption in Europe: A Systematic Review.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Feb 8;17(2):76. doi: 10.3390/toxins17020076. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39998093 Free PMC article.
-
A Hotspot of TTX Contamination in the Adriatic Sea: Study on the Origin and Causative Factors.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 22;21(1):8. doi: 10.3390/md21010008. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662181 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the Anatomical Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Animals.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Aug 22;14(8):576. doi: 10.3390/toxins14080576. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36006238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technical specifications for a EU-wide baseline survey of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from aquaculture animals.EFSA J. 2024 Jul 31;22(7):e8928. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8928. eCollection 2024 Jul. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 39086460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell K., Barnes P., Haughey S., Higgins C., Kawatsu K., Vasconcelos V., Elliott C. Development and Single Laboratory Validation of an Optical Biosensor Assay for Tetrodotoxin Detection as a Tool to Combat Emerging Risks in European Seafood Rapid Detection in Food and Feed. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013;405:7753–7763. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-7106-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

