Antitumor Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid on Human Malignant Glioblastoma Cells
- PMID: 34070493
- PMCID: PMC8199444
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115596
Antitumor Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid on Human Malignant Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
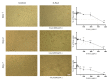
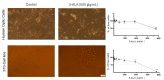
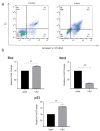
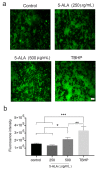
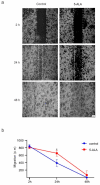
5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) is a naturally occurring non-proteinogenic amino acid, which contributes to the diagnosis and therapeutic approaches of various cancers, including glioblastoma (GBM). In the present study, we aimed to investigate whether 5-ALA exerted cytotoxic effects on GBM cells. We assessed cell viability, apoptosis rate, mRNA expressions of various apoptosis-related genes, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and migration ability of the human U-87 malignant GBM cell line (U87MG) treated with 5-ALA at different doses. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 5-ALA on U87MG cells was 500 μg/mL after 7 days; 5-ALA was not toxic for human optic cells and NIH-3T3 cells at this concentration. The application of 5-ALA led to a significant increase in apoptotic cells, enhancement of Bax and p53 expressions, reduction in Bcl-2 expression, and an increase in ROS generation. Furthermore, the application of 5-ALA increased the accumulation of U87MG cells in the SUB-G1 population, decreased the expression of cyclin D1, and reduced the migration ability of U87MG cells. Our data indicate the potential cytotoxic effects of 5-ALA on U87MG cells. Further studies are required to determine the spectrum of the antitumor activity of 5-ALA on GBM.
Keywords: apoptosis; brain tumor; cell death; protoporphyrin; tumor cell line.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC) induces apoptosis of GBM 8401 human brain glioblastoma multiforms cells via activation of caspase-8/Bid and the reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial pathway.Environ Toxicol. 2016 Dec;31(12):1751-1760. doi: 10.1002/tox.22177. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Environ Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 28675694
-
5-Aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy suppressed survival factors and activated proteases for apoptosis in human glioblastoma U87MG cells.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Mar 30;415(3):242-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.01.071. Epub 2007 Feb 11. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17335970 Free PMC article.
-
Saponin 1 induces apoptosis and suppresses NF-κB-mediated survival signaling in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e81258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081258. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278406 Free PMC article.
-
Magnolol induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells via G0/G1 phase arrest and p53-mediated mitochondrial pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Oct;120(10):17067-17079. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28968. Epub 2019 Jun 3. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31155771
-
Metalloporphyrin Pd(T4) Exhibits Oncolytic Activity and Cumulative Effects with 5-ALA Photodynamic Treatment against C918 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 20;21(2):669. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020669. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31968535 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Sonodynamic Therapy Using a High Throughput 3D Glioblastoma Spheroid Model with 5-ALA and TMZ Sonosensitizers.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Dec;13(32):e2402877. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202402877. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 39434433 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Glioblastoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 28;10(3):564. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030564. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective effect of parthenolide in an in vitro model of Parkinson's disease through its regulation of nuclear factor-kappa B and oxidative stress.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jul 17;51(1):819. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09779-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39017801
-
Effect of combined blue light and 5-ALA on mitochondrial functions and cellular responses in B16F1 melanoma and HaCaT cells.Cytotechnology. 2024 Dec;76(6):795-816. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00654-x. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39435424
-
Immunogenic cell death mediated TLR3/4-activated MSCs in U87 GBM cell line.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 22;10(9):e29858. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29858. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38698968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han S.J., Englot D.J., Birk H., Molinaro A.M., Chang S.M., Clarke J.L., Prados M.D., Taylor J.W., Berger M.S., Butowski N.A. Impact of Timing of Concurrent Chemoradiation for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. Neurosurgery. 2015;62(Suppl. 1):160–165. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000801. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stummer W., Pichlmeier U., Meinel T., Wiestler O.D., Zanella F., Reulen H.-J. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:392–401. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70665-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuhnt D., Becker A., Ganslandt O., Bauer M., Buchfelder M., Nimsky C. Correlation of the extent of tumor volume resection and patient survival in surgery of glioblastoma multiforme with high-field intraoperative MRI guidance. Neuro-Oncology. 2011;13:1339–1348. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor133. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

