Proatherogenic Sialidases and Desialylated Lipoproteins: 35 Years of Research and Current State from Bench to Bedside
- PMID: 34070542
- PMCID: PMC8228531
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9060600
Proatherogenic Sialidases and Desialylated Lipoproteins: 35 Years of Research and Current State from Bench to Bedside
Abstract
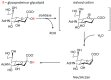
This review summarizes the main achievements in basic and clinical research of atherosclerosis. Focusing on desialylation as the first and the most important reaction of proatherogenic pathological cascade, we speak of how desialylation increases the atherogenic properties of low density lipoproteins and decreases the anti-atherogenic properties of high density lipoproteins. The separate sections of this paper are devoted to immunogenicity of lipoproteins, the enzymes contributing to their desialylation and animal models of atherosclerosis. In addition, we evaluate the available experimental and diagnostic protocols that can be used to develop new therapeutic approaches for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: HDL; LDL; animal models of atherosclerosis; anti-LDL antibodies; apolipoproteins; atherogenesis; desialylation; diagnostics of atherosclerosis; sialidase; trans-sialidase; treatment options for atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Orekhov A.N., Tertov V.V., Mukhin D.N., Mikhailenko I.A. Modification of low density lipoprotein by desialylation causes lipid accumulation in cultured cells: Discovery of desialylated lipoprotein with altered cellular metabolism in the blood of atherosclerotic patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;162:206–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(89)91982-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Orekhov A.N., Tertov V.V., Sobenin I.A., Smirnov V.N., Via D.P., Guevara J., Jr., Gotto A.M., Jr., Morrisett J.D. Sialic acid content of human low density lipoproteins affects their interaction with cell receptors and intracellular lipid accumulation. J. Lipid Res. 1992;33:805–817. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)41506-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

