Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity
- PMID: 34070572
- PMCID: PMC8229270
- DOI: 10.3390/v13060983
Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity
Abstract
Despite the advent of effective, curative treatments for hepatitis C virus (HCV), a preventative vaccine remains essential for the global elimination of HCV. It is now clear that the induction of broadly neutralising antibodies (bNAbs) is essential for the rational design of such a vaccine. This review details the current understanding of epitopes on the HCV envelope, characterising the potency, breadth and immunodominance of antibodies induced against these epitopes, as well as describing the interactions between B-cell receptors and HCV infection, with a particular focus on bNAb heavy and light chain variable gene usage. Additionally, we consider the importance of a public repertoire for antibodies against HCV, compiling current knowledge and suggesting that further research in this area may be critical to the rational design of an effective HCV vaccine.
Keywords: HCV–BCR interactions; antigenic domains; epitope mapping; hepatitis C virus; human monoclonal antibodies; immunodominance; neutralising antibodies; public antibody repertoire; vaccine development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
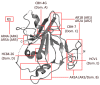

References
-
- WHO . Hepatitis C. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- WHO . Combating Hepatitis B and C to Reach Elimination by 2030. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Grebely J., Page K., Sacks-Davis R., van der Loeff M.S., Rice T.M., Bruneau J., Morris M.D., Hajarizadeh B., Amin J., Cox A.L., et al. The effects of female sex, viral genotype, and IL28B genotype on spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 2014;59:109–120. doi: 10.1002/hep.26639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

