Interactions between an Associative Amphiphilic Block Polyelectrolyte and Surfactants in Water: Effect of Charge Type on Solution Properties and Aggregation
- PMID: 34070596
- PMCID: PMC8197838
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13111729
Interactions between an Associative Amphiphilic Block Polyelectrolyte and Surfactants in Water: Effect of Charge Type on Solution Properties and Aggregation
Abstract
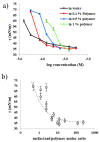
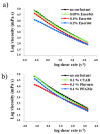
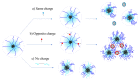
The study of interactions between polyelectrolytes (PE) and surfactants is of great interest for both fundamental and applied research. These mixtures can represent, for example, models of self-assembly and molecular organization in biological systems, but they are also relevant in industrial applications. Amphiphilic block polyelectrolytes represent an interesting class of PE, but their interactions with surfactants have not been extensively explored so far, most studies being restricted to non-associating PE. In this work, interactions between an anionic amphiphilic triblock polyelectrolyte and different types of surfactants bearing respectively negative, positive and no charge, are investigated via surface tension and solution rheology measurements for the first time. It is evidenced that the surfactants have different effects on viscosity and surface tension, depending on their charge type. Micellization of the surfactant is affected by the presence of the polymer in all cases; shear viscosity of polymer solutions decreases in presence of the same charge or nonionic surfactants, while the opposite charge surfactant causes precipitation. This study highlights the importance of the charge type, and the role of the associating hydrophobic block in the PE structure, on the solution behavior of the mixtures. Moreover, a possible interaction model is proposed, based on the obtained data.
Keywords: amphiphilic block copolymers; polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes; polyelectrolytes; rheology; surface activity; surfactants.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gradzielski M., Hoffmann I. Polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes (PESCs) composed of oppositely charged components. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;35:124–141. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2018.01.017. - DOI
-
- Penfold J., Thomas R., Taylor D. Polyelectrolyte/surfactant mixtures at the air–solution interface. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006;11:337–344. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2006.08.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

