Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique
- PMID: 34070815
- PMCID: PMC8229650
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10060654
Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique
Abstract
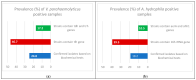
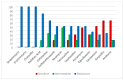
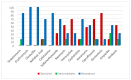
Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila are major public health problems and the main cause of bacterial disease in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). This study was conducted to determine the prevalence, antibiotic resistance and some virulence genes of both V. parahaemolyticus and A. hydrophila isolates from Nile tilapia. From Manzala Farm at Dakahlia governorate, 250 freshwater fish samples were collected. The confirmed bacterial isolates from the examined Nile tilapia samples in the study were 24.8% (62/250) for V. parahaemolyticus and 19.2% (48/250) for A. hydrophila. multiplex PCR, revealing that the tlh gene was found in 46.7% (29/62) of V. parahaemolyticus isolates, while the tdh and trh virulence genes were found in 17.2% (5/29). Meanwhile, 39.5% (19/48) of A. hydrophila isolates had the 16s rRNA gene and 10.5% (2/19) had the aerA and ahh1 virulence genes. The Multiple Antibiotic Resistance indices of V. parahaemolyticus and A. hydrophila were 0.587 and 0.586, respectively. In conclusion, alternative non-antibiotic control strategies for bacterial infections in farmed fish should be promoted to avoid multidrug-resistant bacteria. Therefore, it is suggested that farmers should be skilled in basic fish health control and that molecular detection methods are more rapid and cost-effective than bacteriological methods.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; Oreochromis niloticus; Vibrio parahaemolyticus; molecular identification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of bacterial foodborne pathogens in Nile tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) at points of retail sale in Nairobi, Kenya.Front Antibiot. 2023 May 24;2:1156258. doi: 10.3389/frabi.2023.1156258. eCollection 2023. Front Antibiot. 2023. PMID: 39816642 Free PMC article.
-
Virulent and Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Diseased Nile Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis niloticus) in Egypt with Sequencing of Some Virulence-Associated Genes.Biocontrol Sci. 2021;26(3):167-176. doi: 10.4265/bio.26.167. Biocontrol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34556619
-
Phenotypic, molecular detection, and Antibiotic Resistance Profile (MDR and XDR) of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Farmed Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Mar 8;20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03942-y. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38459543 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of colistin resistance and characterization of antimicrobial resistance and virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila, Salmonella spp., and Vibrio cholerae isolated from hybrid red tilapia cage culture.PeerJ. 2023 Feb 23;11:e14896. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14896. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36855429 Free PMC article.
-
Summer mortality syndrome bacterial pathogens in farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Open Vet J. 2024 Jan;14(1):53-69. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.7. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 38633195 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In-feed oxolinic acid induces oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Apr 4;14:102020. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.102020. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40242397 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on the epidemiology and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Vibrio species in the MENA region, 2000-2023.Future Microbiol. 2024;19(15):1333-1353. doi: 10.1080/17460913.2024.2392460. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Future Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39229784 Review.
-
First Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Migratory Birds in Egypt: Antibiogram, Virulence, and Resistance Gene Profiles Indicating Zoonotic and Public Health Risks.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Nov 27;82(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03992-3. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39601954
-
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from freshwater fishes at Middle Upper Egypt.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 18;15(1):5920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89465-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39966501 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of Methicillin and Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from Cattle, Sheep Carcasses and Slaughterhouse Workers.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;12(2):205. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020205. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soliman N.F., Yacout D.M.M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Status, constraints and potentials. Aquac. Int. 2016;24:1201–1227. doi: 10.1007/s10499-016-9989-9. - DOI
-
- Ayyat M.S., Ayyat A.M.N., Naiel M.A.E., Al-Sagheer A.A. Reversal effects of some safe dietary supplements on lead contaminated diet induced impaired growth and associated parameters in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture. 2020;515:734580. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734580. - DOI
-
- Casadei E., Albert J. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Encycl. Food Health. 2015:749–753. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-384947-2.00270-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

