Exenatide Microspheres for Monthly Controlled-Release Aided by Magnesium Hydroxide
- PMID: 34070856
- PMCID: PMC8226777
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060816
Exenatide Microspheres for Monthly Controlled-Release Aided by Magnesium Hydroxide
Abstract
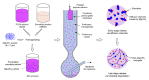
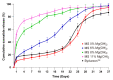
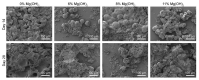
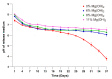
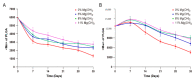
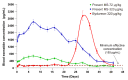
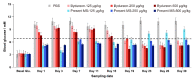
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of diabetes medicines offering self-regulating glycemic efficacy and may best be administrated in long-acting forms. Among GLP-1 receptor agonists, exenatide is the one requiring the least dose so that controlled-release poly(d, l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres may best achieve this purpose. Based on this consideration, the present study extended the injection interval of exenatide microspheres from one week of the current dosage form to four weeks by simply blending Mg(OH)2 powder within the matrix of PLGA microspheres. Mg(OH)2 served as the diffusion channel creator in the earlier stage of the controlled-release period and the decelerator of the self-catalyzed degradation of PLGA (by the formed lactic and glycolic acids) in the later stage due to its pH-responsive solubility. As a result, exenatide gradually diffused from the microspheres through Mg(OH)2-created diffusion channels before degradation of the PLGA matrix, followed by a mild release due to Mg(OH)2-buffered degradation of the polymer skeleton. In addition, an extruding-settling process comprising squeezing the PLGA solution through a porous glass membrane and sedimentation-aided solidification of the PLGA droplets was used to prepare the microspheres to ensure narrow size distribution and 95% encapsulation efficiency in an aqueous continuous phase. A pharmacokinetic study using rhesus monkey model confirmed the above formulation design by showing a steady blood concentration profile of exenatide with reduced CMAX and dosage form index. Mg·(OH)2.
Keywords: PLGA; controlled-release; exenatide; magnesium hydroxide; microsphere.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Yujie Qin is from BioDosage Tech, Ltd.; Tuo Jin is from BioDosage Tech, Ltd. and BioPharm Solutions, Inc., BioDosage Tech, Ltd provided the instrument of microsphere production and BioPharm Solutions, Inc. was involved in the interpretation of data.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preparation of uniform-sized exenatide-loaded PLGA microspheres as long-effective release system with high encapsulation efficiency and bio-stability.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013 Dec 1;112:492-8. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.048. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013. PMID: 24075786
-
Preparation, characterization, and pharmacodynamics of exenatide-loaded poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2010 Nov;58(11):1474-9. doi: 10.1248/cpb.58.1474. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2010. PMID: 21048339
-
Mechanistic studies for monodisperse exenatide-loaded PLGA microspheres prepared by different methods based on SPG membrane emulsification.Acta Biomater. 2014 Oct;10(10):4247-56. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.06.018. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Acta Biomater. 2014. PMID: 24952071
-
Development of composite PLGA microspheres containing exenatide-encapsulated lecithin nanoparticles for sustained drug release.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020 May;15(3):347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32636952 Free PMC article.
-
Microencapsulation of protein drugs for drug delivery: strategy, preparation, and applications.J Control Release. 2014 Nov 10;193:324-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25218676 Review.
Cited by
-
Poly(L-Lactic Acid) Composite with Surface-Modified Magnesium Hydroxide Nanoparticles by Biodegradable Oligomer for Augmented Mechanical and Biological Properties.Materials (Basel). 2021 Oct 7;14(19):5869. doi: 10.3390/ma14195869. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34640265 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Anti-Inflammation of Poly(L-Lactic Acid) by Stereocomplexes of PLLA/PDLA and Surface-Modified Magnesium Hydroxide Nanoparticles.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 10;14(18):3790. doi: 10.3390/polym14183790. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145934 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Innovative Approaches in Type-2 Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Review on Nano-carriers and Transdermal Drug Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(22):1725-1745. doi: 10.2174/0113816128313325240513113840. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38847167 Review.
-
Injectable sustained-release poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres of exenatide prepared by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsion process based on a design of experiment approach.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Jan 2;8(3):e10485. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10485. eCollection 2023 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37206215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawaguchi H. Functional polymer microspheres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000;25:1171–1210. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6700(00)00024-1. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

