Restoring the Oxidase-Like Activity of His@AuNCs for the Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase
- PMID: 34070918
- PMCID: PMC8227771
- DOI: 10.3390/bios11060174
Restoring the Oxidase-Like Activity of His@AuNCs for the Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase
Abstract
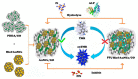
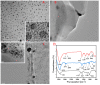
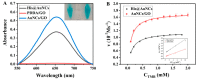
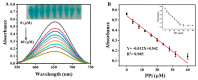
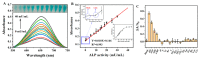
In this paper, we propose a simple colorimetric method for the sensitive and selective detection of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity based on the turn off/turn on oxidase mimic activity of His@AuNCs. His@AuNCs/graphene oxide hybrids (His@AuNCs/GO) were easily obtained using the self-assembly method with poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA)-coated GO and showed high oxidase-like activity compared with His@AuNCs. We found that the pyrophosphate ion (P2O74-, PPi) could effectively inhibit the oxidase mimic activity of His@AuNCs/GO, and the hydrolysis of PPi by ALP restored the inhibited activity of His@AuNCs/GO, enabling them to efficiently catalyze the oxidation of 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) to generate the blue oxidized product oxTMB. The intensity of the color showed a linear dependency with the ALP activity. ALP was detected in the linear range of 0-40 mU/mL with a low detection limit (LOD) of 0.26 mU/mL (S/N = 3). The proposed method is fast, easy, and can be applied to monitor the ALP activity in serum samples accurately and effectively, which suggests its practicability and reliability in the detection of ALP activity in clinical practice.
Keywords: ALP; His@AuNCs/GO; PPi; colorimetric detection; oxidase-like activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fernley H.N. Enzymes. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1971. 18 Mammalian Alkaline Phosphatases; pp. 417–447. - DOI
-
- Couttenye M.M., D’Haese P.C., Van H.V.O., Lemoniatou E., Goodman W., Verpooten G.A., De B.M.E. Low serum levels of alkaline phosphatase of bone origin: A good marker of adynamic bone disease in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1996;11:1065–1072. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ndt.a027457. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

