Metabolites Profiling, In Vitro, In Vivo, Computational Pharmacokinetics and Biological Predictions of Aloe perryi Resins Methanolic Extract
- PMID: 34070945
- PMCID: PMC8227737
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10061106
Metabolites Profiling, In Vitro, In Vivo, Computational Pharmacokinetics and Biological Predictions of Aloe perryi Resins Methanolic Extract
Abstract
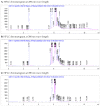
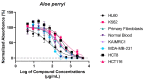
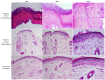
Aloe perryi is a traditional herb that has various biological and pharmacological properties such as anti-inflammatory, laxative, antiviral, antidiabetic, and antitumor effects, which have not been deliberated before. The current investigation aims to evaluate in vitro cytotoxicity against several cancer cell lines in addition to in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of Aloe perryi extract using a rat animal model. Moreover, the pharmacokinetic properties of bioactive constituents and possible biological targets were assessed and evaluated. The methanolic extract of Aloe perryi was prepared by maceration, to tentatively identify the biomolecules of the Aloe perryi extract, analytical LC-QTOF-MS method was employed for Aloe perryi methanolic extract. The cytotoxic activity was examined in six cancer cell lines using Titer-Glo assay and the IC50s were calculated in addition to in silico target predictions and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity assessment. Subsequently, the pharmacokinetics of the identified active components of Aloe perryi were predicted using SwissADME, and target prediction using the Molinspiration webserver. The cytotoxic activity on HL60 and MDA-MB-231 was moderately affected by the Aloe perryi extract with IC50 of 63.81, and 89.85 μg/ml, respectively, with no activity on other cells lines. Moreover, the Aloe perryi extract exhibited a significant increase in wound contraction, hair growth, and complete re-epithelization when compared with the negative control. The pharmacokinetic properties of the bioactive constituents suggested a good pharmaceutical profile for the active compounds and nuclear receptors and enzymes were the two main possible targets for these active compounds. Our results demonstrated the promising activity of Aloe perryi extract with cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory properties, indicating a potential therapeutic utility of this plant in various disease conditions.
Keywords: ADME; Aloe perryi resins methanolic extract; breast cancer; in vivo anti-inflammatory; leukemia cancer; target prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wali A.F., Majid S., Rasool S., Shehada S.B., Abdulkareem S.K., Firdous A., Beigh S., Shakeel S., Mushtaq S., Akbar I., et al. Natural products against cancer: Review on phytochemicals from marine sources in preventing cancer. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019;27:767–777. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.04.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

