Ribosome Biogenesis and Cancer: Overview on Ribosomal Proteins
- PMID: 34071057
- PMCID: PMC8197113
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115496
Ribosome Biogenesis and Cancer: Overview on Ribosomal Proteins
Abstract
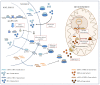
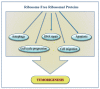
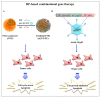
Cytosolic ribosomes (cytoribosomes) are macromolecular ribonucleoprotein complexes that are assembled from ribosomal RNA and ribosomal proteins, which are essential for protein biosynthesis. Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) perform translation of the proteins essential for the oxidative phosphorylation system. The biogenesis of cytoribosomes and mitoribosomes includes ribosomal RNA processing, modification and binding to ribosomal proteins and is assisted by numerous biogenesis factors. This is a major energy-consuming process in the cell and, therefore, is highly coordinated and sensitive to several cellular stressors. In mitochondria, the regulation of mitoribosome biogenesis is essential for cellular respiration, a process linked to cell growth and proliferation. This review briefly overviews the key stages of cytosolic and mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis; summarizes the main steps of ribosome biogenesis alterations occurring during tumorigenesis, highlighting the changes in the expression level of cytosolic ribosomal proteins (CRPs) and mitochondrial ribosomal proteins (MRPs) in different types of tumors; focuses on the currently available information regarding the extra-ribosomal functions of CRPs and MRPs correlated to cancer; and discusses the role of CRPs and MRPs as biomarkers and/or molecular targets in cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer; cancer treatment; mitochondrial ribosomal proteins; mitoribosome biogenesis; ribosomal proteins; ribosome biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

