Achievements in Thermosensitive Gelling Systems for Rectal Administration
- PMID: 34071110
- PMCID: PMC8197127
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115500
Achievements in Thermosensitive Gelling Systems for Rectal Administration
Abstract
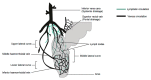
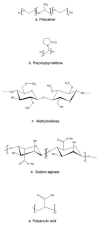
Rectal drug delivery is an effective alternative to oral and parenteral treatments. This route allows for both local and systemic drug therapy. Traditional rectal dosage formulations have historically been used for localised treatments, including laxatives, hemorrhoid therapy and antipyretics. However, this form of drug dosage often feels alien and uncomfortable to a patient, encouraging refusal. The limitations of conventional solid suppositories can be overcome by creating a thermosensitive liquid suppository. Unfortunately, there are currently only a few studies describing their use in therapy. However, recent trends indicate an increase in the development of this modern therapeutic system. This review introduces a novel rectal drug delivery system with the goal of summarising recent developments in thermosensitive liquid suppositories for analgesic, anticancer, antiemetic, antihypertensive, psychiatric, antiallergic, anaesthetic, antimalarial drugs and insulin. The report also presents the impact of various types of components and their concentration on the properties of this rectal dosage form. Further research into such formulations is certainly needed in order to meet the high demand for modern, efficient rectal gelling systems. Continued research and development in this field would undoubtedly further reveal the hidden potential of rectal drug delivery systems.
Keywords: drug delivery system; poloxamer; rectal drug delivery; rectal gel; solid suppository; thermosensitive gel; thermosensitive liquid suppository.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors declare no competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thermally reversible in situ gelling carbamazepine liquid suppository.Drug Deliv. 2006 Mar-Apr;13(2):143-8. doi: 10.1080/10717540500316003. Drug Deliv. 2006. PMID: 16423803
-
Tolmetin sodium-loaded thermosensitive mucoadhesive liquid suppositories for rectal delivery; strategy to overcome oral delivery drawbacks.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Feb;45(2):252-264. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2018.1534858. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30303407
-
Advances in rectal drug delivery systems.Pharm Dev Technol. 2018 Dec;23(10):942-952. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2018.1484766. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Pharm Dev Technol. 2018. PMID: 29888992 Review.
-
Evaluation of epirubicin in thermogelling and bioadhesive liquid and solid suppository formulations for rectal administration.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Dec 31;15(1):342-60. doi: 10.3390/ijms15010342. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24384838 Free PMC article.
-
Rectal route in the 21st Century to treat children.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014 Jun;73:34-49. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 May 25. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014. PMID: 24871671 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermosensitive hydrogel with emodin-loaded triple-targeted nanoparticles for a rectal drug delivery system in the treatment of chronic non-bacterial prostatitis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jan 18;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02282-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38238760 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Rectal In Situ Gel of Meloxicam Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex.Molecules. 2023 May 15;28(10):4099. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104099. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241839 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Angiogenesis and Effect on Inflammatory Bowel Disease of Ginsenoside Rg3-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogel.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 25;16(10):1243. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101243. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458575 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Comprehensive Characteristics of Thermosensitive Liquid Suppositories of Metoprolol Based on Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13743. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213743. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430222 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Functional Applications of Hydrogel Delivery Systems in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Drug Delivery, Anti-Inflammation, and Intestinal Repair.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 22;17(11):1430. doi: 10.3390/polym17111430. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verma P., Thakur A.S., Deshmukh K., Jha D.A.K., Verma S. Routes of drug administration. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2010;1:54–59.
-
- Dumortier G., Grossiord J.L., Zuber M., Couarraze G., Chaumeil J.C. Rheological study of a thermoreversible morphine gel: Drug development and industrial pharmacy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1991;17:1255–1265. doi: 10.3109/03639049109043858. - DOI
-
- Klueglich M., Ring A., Scheuerer S., Trommeshauser D., Schuijt C., Liepold B., Berndl G. Ibuprofen extrudate, a novel, rapidly dissolving ibuprofen formulation: Relative bioavailability compared to ibuprofen lysinate and regular ibuprofen, and food effect on all formulations. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005;45:1055–1061. doi: 10.1177/0091270005279579. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical