Reaction Time and Visual Memory in Connection with Alcohol Use in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder
- PMID: 34071123
- PMCID: PMC8224767
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11060688
Reaction Time and Visual Memory in Connection with Alcohol Use in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder
Abstract
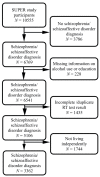
The purpose of this study was to explore the association between cognition and hazardous drinking and alcohol use disorder in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Cognition is more or less compromised in schizophrenia, and schizoaffective disorder and alcohol use might aggravate this phenomenon. The study population included 3362 individuals from Finland with diagnoses of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Hazardous drinking was screened with the AUDIT-C (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test for Consumption) screening tool. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) diagnoses were obtained from national registrar data. Participants performed two computerized tasks from the Cambridge Automated Neuropsychological Test Battery (CANTAB) on a tablet computer: The Five-Choice Serial Reaction Time Task (5-CSRTT) or the reaction time (RT) test and the Paired Associative Learning (PAL) test. The association between alcohol use and the RT and PAL tests was analyzed with log-linear regression and logistic regression, respectively. After adjustment for age, education, housing status, and the age at which the respondents had their first psychotic episodes, hazardous drinking was associated with a lower median RT in females and less variable RT in males, while AUD was associated with a poorer PAL test performance in terms of the total errors adjusted scores (TEASs) in females. Our findings of positive associations between alcohol and cognition in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder are unique.
Keywords: alcohol; cognition; reaction time; schizoaffective disorder; schizophrenia; visual memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bosia M., Buonocore M., Bechi M., Santarelli L., Spangaro M., Cocchi F., Guglielmino C., Bianchi L., Bringheli S., Bosinelli F., et al. Improving Cognition to Increase Treatment Efficacy in Schizophrenia: Effects of Metabolic Syndrome on Cognitive Remediation’s Outcome. Front. Psychiatry. 2018;9:647. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00647. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vacca A., Longo R., Mencar C. Identification and evaluation of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia using “Machine learning”. Psychiatr. Danub. 2019;31:261–264. - PubMed
-
- Anda L., Brønnick K.K., Johannessen J.O., Joa I., Kroken R.A., Johnsen E., Rettenbacher M., Fathian F., Løberg E.-M. Cognitive Profile in Ultra High Risk for Psychosis and Schizophrenia: A Comparison Using Coordinated Norms. Front. Psychiatry. 2019;10:695. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00695. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Potvin S., Stavro K., Pelletier J. Paradoxical Cognitive Capacities in Dual Diagnosis Schizophrenia: The Quest for Explanatory Factors. J. Dual Diagn. 2012;8:35–47. doi: 10.1080/15504263.2012.648549. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources