A Multiomic Approach to Understand How Pleurotus eryngii Transforms Non-Woody Lignocellulosic Material
- PMID: 34071235
- PMCID: PMC8227661
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7060426
A Multiomic Approach to Understand How Pleurotus eryngii Transforms Non-Woody Lignocellulosic Material
Abstract
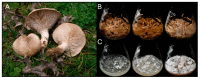
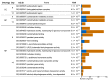
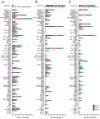
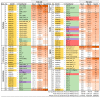
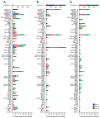
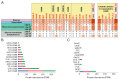
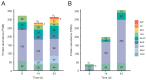
Pleurotus eryngii is a grassland-inhabiting fungus of biotechnological interest due to its ability to colonize non-woody lignocellulosic material. Genomic, transcriptomic, exoproteomic, and metabolomic analyses were combined to explain the enzymatic aspects underlaying wheat-straw transformation. Up-regulated and constitutive glycoside-hydrolases, polysaccharide-lyases, and carbohydrate-esterases active on polysaccharides, laccases active on lignin, and a surprisingly high amount of constitutive/inducible aryl-alcohol oxidases (AAOs) constituted the suite of extracellular enzymes at early fungal growth. Higher enzyme diversity and abundance characterized the longer-term growth, with an array of oxidoreductases involved in depolymerization of both cellulose and lignin, which were often up-regulated since initial growth. These oxidative enzymes included lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) acting on crystalline polysaccharides, cellobiose dehydrogenase involved in LPMO activation, and ligninolytic peroxidases (mainly manganese-oxidizing peroxidases), together with highly abundant H2O2-producing AAOs. Interestingly, some of the most relevant enzymes acting on polysaccharides were appended to a cellulose-binding module. This is potentially related to the non-woody habitat of P. eryngii (in contrast to the wood habitat of many basidiomycetes). Additionally, insights into the intracellular catabolism of aromatic compounds, which is a neglected area of study in lignin degradation by basidiomycetes, were also provided. The multiomic approach reveals that although non-woody decay does not result in dramatic modifications, as revealed by detailed 2D-NMR and other analyses, it implies activation of the complete set of hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes characterizing lignocellulose-decaying basidiomycetes.
Keywords: Pleurotus eryngii; carbohydrate-active enzymes; lignin-modifying enzymes; lignocellulose transformation; metabolomics; oxidoreductases; proteomics; solid-state fermentation; transcriptomics; wheat–straw.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Dahmen N., Lewandowski I., Zibek S., Weidtmann A. Integrated lignocellulosic value chains in a growing bioeconomy: Status quo and perspectives. GCB Bioenergy. 2019;11:107–117. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12586. - DOI
-
- Kobayashi A., Fukuoka A. Synthesis and utilisation of sugar compounds derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2013;15:1740–1763. doi: 10.1039/c3gc00060e. - DOI

