Development and Optimization of Supercritical Fluid Extraction Setup Leading to Quantification of 11 Cannabinoids Derived from Medicinal Cannabis
- PMID: 34071473
- PMCID: PMC8227983
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10060481
Development and Optimization of Supercritical Fluid Extraction Setup Leading to Quantification of 11 Cannabinoids Derived from Medicinal Cannabis
Abstract
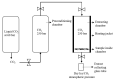
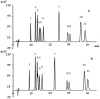
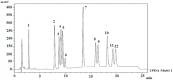
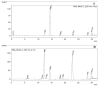
In this study, the optimal setup of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) was designed and developed, leading to the quantitation of 11 distinct cannabinoids (cannabidivann (CBDV), tetrahydrocannabivann (THCV), cannabidiol (CBD), cannabigerol (CBG) cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabinol (CBN), delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC), cannabichomere (CBC) and delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol acid (THCA-A)) extracted from the flowers of medicinal cannabis (sp. Sativa). Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) extraction was performed at 37 °C, a pressure of 250 bar with the maximum theoretical density of CO2 (893.7 kg/m3), which generated the highest yield of cannabinoids from the flower-derived extract. Additionally, a cold separator (separating chamber) was used and positioned immediately after the sample containing chamber to maximize the yield. It was also found that successive washing of the extract with fresh scCO2 further increased yields. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with DAD (uHPLC-DAD) was used to develop a method for the quantification of 11 cannabinoids. The C18 stationary phase was used in conjunction with a two solvent system gradient program resulting in the acquisition of the well-resolved chromatogram over a timespan of 32 min. The accuracy and precision of isolated cannabinoids across inter-and intra-day periods were within acceptable limits (<±15%). The assay was also fully validated and deemed sensitive from linearity, LOQ, and LOD perspective. The findings of this body of work are expected to facilitate improved conditions for the optimal extraction of select cannabinoids using scCO2, which holds promise in the development of well-characterized medicinal cannabis formulations. As to our best knowledge, this is the first study to report the uHPLC quantification method for the analysis of 11 cannabinoids from scCO2 extract in a single run with more than 1 min peak separation.
Keywords: SFE Helix unit; SFE Nottingham unit; cannabis flowers; neutral cannabinoids (sp. Sativa); supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2); supercritical extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
[Determination of 11 Cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. by Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (LC-Q-TOF-MS)].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2023;143(4):411-418. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.22-00198. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2023. PMID: 37005243 Japanese.
-
Determination of 11 Cannabinoids in Biomass and Extracts of Different Varieties of Cannabis Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography.J AOAC Int. 2015 Nov-Dec;98(6):1523-8. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.15-095. J AOAC Int. 2015. PMID: 26651563
-
Development and Validation of a GC-FID Method for the Quantitation of 20 Different Acidic and Neutral Cannabinoids.Planta Med. 2023 May;89(6):683-696. doi: 10.1055/a-1962-8165. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Planta Med. 2023. PMID: 36257598
-
Extraction of medicinal cannabinoids through supercritical carbon dioxide technologies: A review.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021 Mar 15;1167:122581. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122581. Epub 2021 Feb 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33639334 Review.
-
Recent advances in Cannabis sativa research: biosynthetic studies and its potential in biotechnology.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2007 Aug;8(4):237-43. doi: 10.2174/138920107781387456. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17691992 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-Dispersion Delivery Systems with Solubilizing Carriers Improving the Solubility and Permeability of Cannabinoids (Cannabidiol, Cannabidiolic Acid, and Cannabichromene) from Cannabis sativa (Henola Variety) Inflorescences.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 4;15(9):2280. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092280. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765249 Free PMC article.
-
Supercritical Extract of Cannabis sativa Inhibits Lung Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Increasing AMPK and MAPKs-Mediated Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 28;14(21):4548. doi: 10.3390/nu14214548. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364815 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the novel and green-assisted techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from millets: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2024 May 11;10(10):e30921. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30921. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38784533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent HPLC-UV Approaches for Cannabinoid Analysis: From Extraction to Method Validation and Quantification Compliance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 24;18(6):786. doi: 10.3390/ph18060786. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terpenes and Cannabinoids in Supercritical CO2 Extracts of Industrial Hemp Inflorescences: Optimization of Extraction, Antiradical and Antibacterial Activity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 7;15(9):1117. doi: 10.3390/ph15091117. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berning A., Compton R., Wochinger K. Results of the 2013-2014 national roadside survey of alcohol and drug use by drivers. J. Drug Addict. Educ. Erad. 2015;11:47.
-
- Brighenti V., Pellati F., Steinbach M., Maran D., Benvenuti S. Development of a new extraction technique and HPLC method for the analysis of non-psychoactive cannabinoids in fibre-type Cannabis sativa L. (hemp) J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017;143:228–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.05.049. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

