Phase I Trial of Prophylactic Donor-Derived IL-2-Activated NK Cell Infusion after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation from a Matched Sibling Donor
- PMID: 34071607
- PMCID: PMC8198961
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112673
Phase I Trial of Prophylactic Donor-Derived IL-2-Activated NK Cell Infusion after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation from a Matched Sibling Donor
Abstract
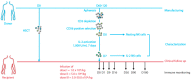
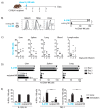
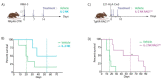
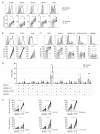
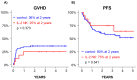
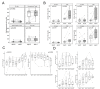
Background: NK cell-based immunotherapy to prevent relapse after allogeneic transplantation is an appealing strategy because NK cells can provide strong antitumor effect without inducing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Thus, we designed a phase-I clinical trial evaluating the safety of a prophylactic donor-derived ex vivo IL-2 activated NK cell (IL-2 NK) infusion after allo-HSCT for patients with hematologic malignancies. Methods: Donor NK cells were purified and cultured ex vivo with IL-2 before infusion, at three dose levels. To identify the maximum tolerated dose was the main objective. In addition, we performed phenotypical and functional characterization of the NK cell therapy product, and longitudinal immune monitoring of NK cell phenotype in patients. Results: Compared to unstimulated NK cells, IL-2 NK cells expressed higher levels of activating receptors and exhibited increased degranulation and cytokine production in vitro. We treated 16 patients without observing any dose-limiting toxicity. At the last follow up, 11 out of 16 treated patients were alive in complete remission of hematologic malignancies without GVHD features and immunosuppressive treatment. Conclusions: Prophylactic donor-derived IL-2 NK cells after allo-HSCT is safe with low incidence of GVHD. Promising survivals and IL-2 NK cell activated phenotype may support a potential clinical efficacy of this strategy.
Keywords: IL-2-activated NK cells; allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; antitumor immunity; cellular immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
E.V. is an employee and shareholder of Innate Pharma. S.U. is shareholder of Innate Pharma. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lee C.J., Savani B.N., Mohty M., Gorin N.C., Labopin M., Ruggeri A., Schmid C., Baron F., Esteve J., Giebel S., et al. Post-Remission Strategies for the Prevention of Relapse Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for High-Risk Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Expert Review from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54:519–530. doi: 10.1038/s41409-018-0286-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsirigotis P., Byrne M., Schmid C., Baron F., Ciceri F., Esteve J., Gorin N.C., Giebel S., Mohty M., Savani B.N., et al. Relapse of AML after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Methods of Monitoring and Preventive Strategies. A Review from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:1431–1438. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2016.167. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kolb H.J., Schattenberg A., Goldman J.M., Hertenstein B., Jacobsen N., Arcese W., Ljungman P., Ferrant A., Verdonck L., Niederwieser D., et al. Graft-versus-Leukemia Effect of Donor Lymphocyte Transfusions in Marrow Grafted Patients. Blood. 1995;86:2041–2050. doi: 10.1182/blood.V86.5.2041.bloodjournal8652041. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

