D-Penicillamine: The State of the Art in Humans and in Dogs from a Pharmacological and Regulatory Perspective
- PMID: 34071639
- PMCID: PMC8229433
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10060648
D-Penicillamine: The State of the Art in Humans and in Dogs from a Pharmacological and Regulatory Perspective
Abstract
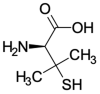
Chelant agents are the mainstay of treatment in copper-associated hepatitis in humans, where D-penicillamine is the chelant agent of first choice. In veterinary medicine, the use of D-penicillamine has increased with the recent recognition of copper-associated hepatopathies that occur in several breeds of dogs. Although the different regulatory authorities in the world (United States Food and Drugs Administration-U.S. FDA, European Medicines Agency-EMEA, etc.) do not approve D-penicillamine for use in dogs, it has been used to treat copper-associated hepatitis in dogs since the 1970s, and is prescribed legally by veterinarians as an extra-label drug to treat this disease and alleviate suffering. The present study aims to: (a) address the pharmacological features; (b) outline the clinical scenario underlying the increased interest in D-penicillamine by overviewing the evolution of its main therapeutic goals in humans and dogs; and finally, (c) provide a discussion on its use and prescription in veterinary medicine from a regulatory perspective.
Keywords: D-penicillamine; copper-associated hepatitis; dog; humans; prescription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lipsky P.E., Ziff M. The effect of D-penicillamine on mitogen-induced human lymphocyte proliferation: Synergistic inhibition by D-penicillamine and copper salts. J. Immunol. 1978;120:1006–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources