Effect of Different Plants on the Growth and Reproduction of Thrips flavus (Thysanoptera: Thripidae)
- PMID: 34071657
- PMCID: PMC8228280
- DOI: 10.3390/insects12060502
Effect of Different Plants on the Growth and Reproduction of Thrips flavus (Thysanoptera: Thripidae)
Abstract
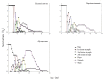
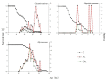
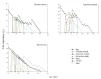
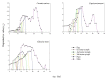
Host plants play an important role in affecting insect development and reproduction. Understanding the host plant preferences is important for pest control. Thrips flavus Schrank (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) is a worldwide phytophagous pest in Palearctic Asian and European countries. We used a life table analysis to study the development duration, population parameters, and population growth of T. flavus on five plant species, including Solanum melongena (Solanaceae), Capsicum annuum (Solanaceae), Glycine max (Leguminosae), Brassica rapa var. glabra (Cruciferae), and Cucumis sativus (Cucurbitaceae). The results showed that T. flavus can survive and reproduce on Cu. sativus and G. max, which were two potentially suitable host plants. T. flavus preferred to oviposit on Cu. sativus with a shorter duration of development (17.8 days) at 25 °C. Therefore, the host plant was an important factor influencing the development and fecundity of T. flavus populations. These results will improve our understanding of the population dynamics of T. flavus and facilitate the development of more scientific and efficient measures to control thrips.
Keywords: Thrips flavus; development; host plant; life table; population growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Population Performance of Thrips hawaiiensis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on Different Vegetable Host Plants.Neotrop Entomol. 2021 Dec;50(6):923-928. doi: 10.1007/s13744-021-00914-x. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Neotrop Entomol. 2021. PMID: 34586610
-
Development and reproduction of Scirtothrips dorsalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on six host plant species.J Econ Entomol. 2024 Aug 12;117(4):1439-1446. doi: 10.1093/jee/toae121. J Econ Entomol. 2024. PMID: 38824446
-
Responses of Thrips hawaiiensis and Thrips flavus populations to elevated CO2 concentrations.J Econ Entomol. 2023 Apr 24;116(2):416-425. doi: 10.1093/jee/toad026. J Econ Entomol. 2023. PMID: 36895199
-
Host Plant Association and Distribution of the Onion Thrips, Thrips tabaci Cryptic Species Complex.Insects. 2022 Mar 17;13(3):298. doi: 10.3390/insects13030298. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35323598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Onion thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae): a global pest of increasing concern in onion.J Econ Entomol. 2011 Feb;104(1):1-13. doi: 10.1603/ec10269. J Econ Entomol. 2011. PMID: 21404832 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Composition of Five Lamiaceae Essential Oils and Their Insecticidal and Phytotoxic Activity.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;13(16):2204. doi: 10.3390/plants13162204. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204640 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse sources of resistance to Thrips palmi (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in chili (Capsicum annuum and C. chinense).J Econ Entomol. 2025 Aug 29;118(4):1942-1949. doi: 10.1093/jee/toaf168. J Econ Entomol. 2025. PMID: 40587379 Free PMC article.
-
An Investigation into the Biological Activities of Four Lamiaceae Essential Oils Against Thrips flavus, Crops, and Weeds.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;14(3):448. doi: 10.3390/plants14030448. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943010 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity and Efficacy of Thirty Insecticides Against Thrips flavus in Northeast China: Laboratory, Semifield, and Field Trials.Insects. 2025 Apr 11;16(4):405. doi: 10.3390/insects16040405. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40332867 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Different Thiamethoxam Concentrations on Riptortus pedestris Development and Fecundity.Toxics. 2024 Jun 26;12(7):460. doi: 10.3390/toxics12070460. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39058112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh S.J., Krishnareddy M. Thrips flavus Schrank (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), a new insect vector of a tospovirus infecting watermelon in India. [(accessed on 27 May 2021)];Pest Manag. Hortic. Ecosyst. 1995 1:115–118. Available online: http://aapmhe.in/index.php/pmhe/article/view/280.
-
- Nickle D.A. Commonly intercepted thrips at US ports of entry from Africa, Europe, and the Mediterranean. III. The genus Thrips Linnaeus, 1758 (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2008;110:165–185. doi: 10.4289/0013-8797-110.1.165. - DOI
-
- Raspudić E., Ivezić M., Jenser G. Check list on Thysanoptera in Croatia. [(accessed on 27 May 2021)];Entomol. Croat. 2003 7:35–41. Available online: http://bib.irb.hr/prikazi-rad?rad=145941.
-
- Tillekaratne K., Edirisinghe J.P., Gunatilleke C.V.S., Karunaratne W.A.I.P. Survey of thrips in Sri Lanka: A checklist of thrips species, their distribution and host plants. Ceylon J. Sci. Biol. Sci. 2011;40:89–108. doi: 10.4038/cjsbs.v40i2.3926. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

