Chicken Heat Shock Protein 70 Is an Essential Host Protein for Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Infection In Vitro
- PMID: 34071696
- PMCID: PMC8229272
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10060664
Chicken Heat Shock Protein 70 Is an Essential Host Protein for Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Infection In Vitro
Abstract
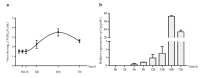
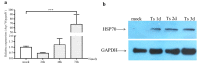
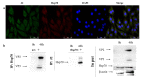
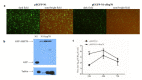
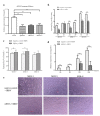
Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) infection causes pathogenicity and mortality in chickens, leading to huge economic losses in the poultry industry worldwide. Studies of host-virus interaction can help us to better understand the viral pathogenicity. As a highly conservative host factor, heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is observed to be involved in numerous viral infections. However, there is little information about the role of chicken Hsp70 (cHsp70) in IBDV infection. In the present study, the increased expression of cHsp70 was observed during IBDV-infected DF-1 cells. Further studies revealed that Hsp70 had similar locations with the viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), and the result of pull-down assay showed the direct interaction between cHsp70 with dsRNA, viral proteins (vp)2 and 3, indicating that maybe cHsp70 participates in the formation of the replication and transcription complex. Furthermore, overexpression of cHsp70 promoted IBDV production and knockdown of cHsp70 using small interfering RNAs (siRNA) and reducedviral production, implying the necessity of cHsp70 in IBDV infection. These results reveal that cHsp70 is essential for IBDV infection in DF-1 cells, suggesting that targeting cHsp70 may be applied as an antiviral strategy.
Keywords: Hsp70; IBDV; dsRNA; host-virus interaction; replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective efficacy of a DNA vaccine construct encoding the VP2 gene of infectious bursal disease and a truncated HSP70 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in chickens.Vaccine. 2015 Feb 18;33(8):1033-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25596458
-
Epigenetic Upregulation of Chicken MicroRNA-16-5p Expression in DF-1 Cells following Infection with Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) Enhances IBDV-Induced Apoptosis and Viral Replication.J Virol. 2020 Jan 6;94(2):e01724-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01724-19. Print 2020 Jan 6. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694944 Free PMC article.
-
GATA3 Inhibits Viral Infection by Promoting MicroRNA-155 Expression.J Virol. 2022 Apr 13;96(7):e0188821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01888-21. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35319228 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbated Apoptosis of Cells Infected with Infectious Bursal Disease Virus upon Exposure to Interferon Alpha.J Virol. 2018 May 14;92(11):e00364-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00364-18. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29540594 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious Bursal Disease: a complex host-pathogen interaction.Dev Comp Immunol. 2013 Nov;41(3):429-38. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.03.017. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23567344 Review.
References
-
- McFerran J.B., McNulty M.S., McKillop E.R., Connor T.J., McCracken R.M., Collins D.S., Allan G.M. Isolation and serological studies with infectious bursal disease viruses from fowl, turkeys and ducks: Demonstration of a second serotype. Avian Pathol. 1980;9:395–404. doi: 10.1080/03079458008418423. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laura B., Nicolás R., Fernando M., Elisabet D.-B., Oscar C.-R., Daniel F., Liliana L.C.-G., Céline C., Nicolas E., Sébastien M.S., et al. Type I interferon acts as a major barrier to the establishment of persistent infectious bursal disease virus infections. J. Virol. 2021;95:e2017–e2020. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

