Effect of Active Coatings Containing Lippa citriodora Kunth. Essential Oil on Bacterial Diversity and Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation in Refrigerated Large Yellow Croaker
- PMID: 34071698
- PMCID: PMC8198210
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13111787
Effect of Active Coatings Containing Lippa citriodora Kunth. Essential Oil on Bacterial Diversity and Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation in Refrigerated Large Yellow Croaker
Abstract
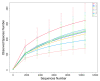
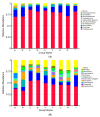
The research evaluated the effects of locust bean gum (LBG) and sodium alginate (SA) active coatings containing 0.15, 0.30 or 0.60% lemon verbena (Lippa citriodora Kunth.) essential oil (LVEO) on the bacterial diversity and myofibrillar proteins (MPs) of large yellow croaker during refrigerated storage at 4 °C for 18 days. Variability in the dominant bacterial community in different samples on the 0, 9th and 18th day was observed. Pseudomonas and Shewanella were the two major genera identified during refrigerated storage. At the beginning, the richness of Pseudomonas was about 37.31% and increased for control (CK) samples during refrigerated storage, however, the LVEO-treated samples increased sharply from day 0 to the 9th day and then decreased. LBG-SA coatings containing LVEO treatments significantly delayed MPs oxidation by retarding the formation of free carbonyl compounds and maintaining higher sulfhydryl content, higher Ca2+-ATPase activity, better organized secondary (higher contents of α-helix and β-sheet) and tertiary structures during refrigerated storage. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) images showed that the integrity of the sarcomere was damaged; the boundaries of the H-, A-, and I-bands, Z-disk, and M-line were fuzzy in the CK samples at the end of storage. However, the LVEO-treated samples were still regular in appearance with distinct dark A-bands, light I-bands, and Z-disk. In brief, LBG-SA active coatings containing LVEO treatments suggested a feasible method for protecting the MPs of large yellow croaker during refrigerated storage.
Keywords: active coating; bacterial diversity; large yellow croaker; lemon verbena essential oil; myofibrillar proteins structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hao T., Li J., Liu Q., Cui K., Chen Q., Xu D., Liu Y., Zhao Y., Mai K., Ai Q. Fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36) in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea): Molecular cloning, characterization and the response to dietary fatty acids. Aquaculture. 2020;528:735557. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735557. - DOI
-
- Lan W.Q., Sun Y.Q., Zhang N.N., Xie J. Effects of epsilon-polylysine and rosemary extract on quality attributes and microbial communities in vacuum-packaged large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) during ice storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s10068-021-00880-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

