A Review of Deep Learning-Based Contactless Heart Rate Measurement Methods
- PMID: 34071736
- PMCID: PMC8198867
- DOI: 10.3390/s21113719
A Review of Deep Learning-Based Contactless Heart Rate Measurement Methods
Abstract
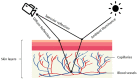
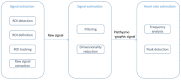
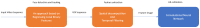
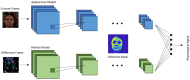
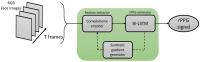
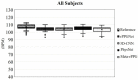
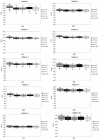
The interest in contactless or remote heart rate measurement has been steadily growing in healthcare and sports applications. Contactless methods involve the utilization of a video camera and image processing algorithms. Recently, deep learning methods have been used to improve the performance of conventional contactless methods for heart rate measurement. After providing a review of the related literature, a comparison of the deep learning methods whose codes are publicly available is conducted in this paper. The public domain UBFC dataset is used to compare the performance of these deep learning methods for heart rate measurement. The results obtained show that the deep learning method PhysNet generates the best heart rate measurement outcome among these methods, with a mean absolute error value of 2.57 beats per minute and a mean square error value of 7.56 beats per minute.
Keywords: deep learning; heart rate measurement methods; remote PPG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Methods for Remote Heart Rate Measurement: A Review and Future Research Agenda.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Sep 20;21(18):6296. doi: 10.3390/s21186296. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KID-PPG: Knowledge Informed Deep Learning for Extracting Heart Rate From a Smartwatch.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025 Mar;72(3):870-877. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3477275. Epub 2025 Feb 20. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39383068
-
PPGnet: Deep Network for Device Independent Heart Rate Estimation from Photoplethysmogram.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2019 Jul;2019:1899-1902. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2019.8856989. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2019. PMID: 31946269
-
CorNET: Deep Learning Framework for PPG-Based Heart Rate Estimation and Biometric Identification in Ambulant Environment.IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2019 Apr;13(2):282-291. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2892297. Epub 2019 Jan 10. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2019. PMID: 30629514
-
Deep learning and remote photoplethysmography powered advancements in contactless physiological measurement.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 17;12:1420100. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1420100. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39104628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Affective State during Physiotherapy and Its Analysis Using Machine Learning Methods.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 16;21(14):4853. doi: 10.3390/s21144853. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34300591 Free PMC article.
-
An Evaluation of Non-Contact Photoplethysmography-Based Methods for Remote Respiratory Rate Estimation.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;23(7):3387. doi: 10.3390/s23073387. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050444 Free PMC article.
-
A System for Monitoring Animals Based on Behavioral Information and Internal State Information.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 16;14(2):0. doi: 10.3390/ani14020281. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254450 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Features and Potential Applications of PPG Signal in Healthcare: A Systematic Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;10(3):547. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10030547. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capturing the pulse: a state-of-the-art review on camera-based jugular vein assessment.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Nov 28;14(12):6470-6492. doi: 10.1364/BOE.507418. eCollection 2023 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 38420308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Madhav K.V., Ram M.R., Krishna E.H., Reddy K.N., Reddy K.A. Estimation of respiratory rate from principal components of photoplethysmographic signals; Proceedings of the IEEE EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES); Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. 30 November 2010; pp. 311–314. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

