Preparation and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies with High Affinity and Broad Class Specificity against Zearalenone and Its Major Metabolites
- PMID: 34071768
- PMCID: PMC8228353
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13060383
Preparation and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies with High Affinity and Broad Class Specificity against Zearalenone and Its Major Metabolites
Abstract
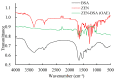
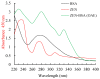
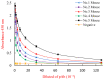
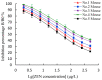
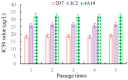
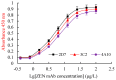
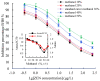
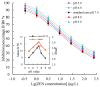
This study aimed to detect and monitor total Zearalenone (ZEN) and its five homologs (ZENs) in cereals and feed. The monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with a high affinity and broad class specificity against ZENs were prepared, and the conditions of a heterologous indirect competitive ELISA (icELISA) were preliminarily optimized based on the ZEN mAbs. The immunogen ZEN-BSA was synthesized using the oxime active ester method (OAE) and identified using infrared (IR) and ultraviolet (UV). The coating antigen ZEN-OVA was obtained via the 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether method (BDE). Balb/c mice were immunized using a high ZEN-BSA dose with long intervals and at multiple sites. A heterologous indirect non-competitive ELISA (inELISA) and an icELISA were used to screen the suitable cell fusion mice and positive hybridoma cell lines. The ZEN mAbs were prepared by inducing ascites in vivo. The standard curve was established, and the sensitivity and specificity of the ZEN mAbs were determined under the optimized icELISA conditions. ZEN-BSA was successfully synthesized at a conjugation ratio of 17.2:1 (ZEN: BSA). Three hybridoma cell lines, 2D7, 3C2, and 4A10, were filtered, and their mAbs corresponded to an IgG1 isotype with a κ light chain. The mAbs titers were between (2.56 to 5.12) × 102 in supernatants and (1.28 to 5.12) × 105 in the ascites. Besides, the 50% inhibitive concentration (IC50) values were from 18.65 to 31.92 μg/L in the supernatants and 18.12 to 31.46 μg/L in the ascites. The affinity constant (Ka) of all of the mAbs was between 4.15 × 109 and 6.54 × 109 L/mol. The IC50 values of mAb 2D7 for ZEN, α-ZEL, β-ZEL, α-ZAL, β-ZAL and ZAN were 17.23, 16.71, 18.27, 16.39, 20.36 and 15.01 μg/L, and their cross-reactivities (CRs, %) were 100%, 103.11%, 94.31%, 105.13%, 84.63%, and 114.79%, respectively, under the optimized icELISA conditions. The limit of detection (LOD) for ZEN was 0.64 μg/L, and its linear working range was between 1.03 and 288.55 μg/L. The mAbs preparation and the optimization of icELISA conditions promote the potential development of a rapid test ELISA kit, providing an alternative method for detecting ZEN and its homologs in cereals and feed.
Keywords: high affinity and broad class specificity; icELISA; immunoassay; immunogen; monoclonal antibodies; zearalenone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

