Optical Constants and Structural Properties of Epitaxial MoS2 Monolayers
- PMID: 34071775
- PMCID: PMC8227853
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11061411
Optical Constants and Structural Properties of Epitaxial MoS2 Monolayers
Abstract
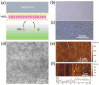
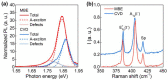
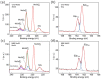
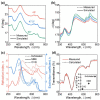
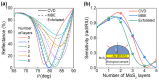
Two-dimensional layers of transition-metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have been widely studied owing to their exciting potential for applications in advanced electronic and optoelectronic devices. Typically, monolayers of TMDs are produced either by mechanical exfoliation or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). While the former produces high-quality flakes with a size limited to a few micrometers, the latter gives large-area layers but with a nonuniform surface resulting from multiple defects and randomly oriented domains. The use of epitaxy growth can produce continuous, crystalline and uniform films with fewer defects. Here, we present a comprehensive study of the optical and structural properties of a single layer of MoS2 synthesized by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) on a sapphire substrate. For optical characterization, we performed spectroscopic ellipsometry over a broad spectral range (from 250 to 1700 nm) under variable incident angles. The structural quality was assessed by optical microscopy, atomic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and Raman spectroscopy through which we were able to confirm that our sample contains a single-atomic layer of MoS2 with a low number of defects. Raman and photoluminescence spectroscopies revealed that MBE-synthesized MoS2 layers exhibit a two-times higher quantum yield of photoluminescence along with lower photobleaching compared to CVD-grown MoS2, thus making it an attractive candidate for photonic applications.
Keywords: MoS2 monolayer; dielectric properties; molecular beam epitaxy; nanophotonics; optical constants; refractive index; spectroscopic ellipsometry; transition-metal dichalcogenides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transition metal dichalcogenides and beyond: synthesis, properties, and applications of single- and few-layer nanosheets.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Jan 20;48(1):56-64. doi: 10.1021/ar5002846. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25490673
-
A Novel Carbon-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition Growth of Large-Area Uniform Monolayer MoS2 and WS2.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Sep 17;11(9):2423. doi: 10.3390/nano11092423. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34578743 Free PMC article.
-
Layer-Controlled Chemical Vapor Deposition Growth of MoS2 Vertical Heterostructures via van der Waals Epitaxy.ACS Nano. 2016 Jul 26;10(7):7039-46. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b03112. Epub 2016 Jul 7. ACS Nano. 2016. PMID: 27373305
-
Molecular beam epitaxy and other large-scale methods for producing monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides.J Phys Condens Matter. 2024 Jun 27;36(38). doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ad5a5d. J Phys Condens Matter. 2024. PMID: 38901422 Review.
-
Conductive Atomic Force Microscopy of Semiconducting Transition Metal Dichalcogenides and Heterostructures.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Apr 22;10(4):803. doi: 10.3390/nano10040803. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32331313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Additive Optical Response in Transition Metal Dichalcogenides Heterostructures.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;12(24):4436. doi: 10.3390/nano12244436. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558289 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in MoS2-Based Biosensors: From Material Fabrication and Characterization to Biomedical, Environmental, and Industrial Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;15(6):371. doi: 10.3390/bios15060371. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical Anisotropy and Excitons in MoS2 Interfaces for Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;12(8):582. doi: 10.3390/bios12080582. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36004977 Free PMC article.
-
Broadband Optical Constants and Nonlinear Properties of SnS2 and SnSe2.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Dec 31;12(1):141. doi: 10.3390/nano12010141. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35010091 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of spin-orbit coupling on optical properties of monolayer [Formula: see text] due to mechanical strains.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 20;13(1):1159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28258-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36670164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mak K.F., Shan J. Photonics and Optoelectronics of 2D Semiconductor Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Nat. Photonics. 2016;10:216–226. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.282. - DOI
-
- Datta I., Chae S.H., Bhatt G.R., Tadayon M.A., Li B., Yu Y., Park C., Park J., Cao L., Basov D.N., et al. Low-Loss Composite Photonic Platform Based on 2D Semiconductor Monolayers. Nat. Photonics. 2020;14:256–262. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-0590-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

