Application of Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Cascade Technology in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 34071794
- PMCID: PMC8199020
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115698
Application of Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Cascade Technology in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
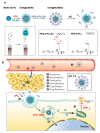
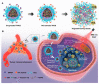
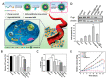
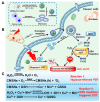
In the current cancer treatment, various combination therapies have been widely used, such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) combined with chemokinetic therapy (CDT). However, due to the complexity of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the limitations of treatment, the efficacy of current treatment options for some cancers is unsatisfactory. Nowadays, cascade technology has been used in cancer treatment and achieved good therapeutic effect. Cascade technology based on nanotechnology can trigger cascade reactions under specific tumor conditions to achieve precise positioning and controlled release, or amplify the efficacy of each drug to improve anticancer efficacy and reduce side effects. Compared with the traditional treatment, the application of cascade technology has achieved the controllability, specificity, and effectiveness of cancer treatment. This paper reviews the application of cascade technology in drug delivery, targeting, and release via nano-drug delivery systems in recent years, and introduces their application in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced cancer treatment. Finally, we briefly describe the current challenges and prospects of cascade technology in cancer treatment in the future.
Keywords: cascade technology; combination therapy; multidrug resistance; tumor microenvironment response.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Advancements in Nanocarrier Delivery Systems for Photodynamic Therapy in Lung Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 May 29;20:6853-6874. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S521444. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40458748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoplatform-based cascade engineering for cancer therapy.Chem Soc Rev. 2020 Dec 21;49(24):9057-9094. doi: 10.1039/d0cs00607f. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Chem Soc Rev. 2020. PMID: 33112326 Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery Systems in Photodynamic Therapy of Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 17;22(22):12405. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212405. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NIR-triggered high-efficient photodynamic and chemo-cascade therapy using caspase-3 responsive functionalized upconversion nanoparticles.Biomaterials. 2017 Oct;141:40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.06.031. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28666101
-
Programmable therapeutic nanoscale covalent organic framework for photodynamic therapy and hypoxia-activated cascade chemotherapy.Acta Biomater. 2022 Sep 1;149:297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.07.003. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35811069
Cited by
-
Potential Use of the Cholesterol Transfer Inhibitor U18666A as a Potent Research Tool for the Study of Cholesterol Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;61(6):3503-3527. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03798-7. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37995080 Review.
-
Tetracycline-grafted mPEG-PLGA micelles for bone-targeting and osteoporotic improvement.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 14;13:993095. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.993095. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188546 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Cell Cycle Regulation on Chemotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 28;22(13):6923. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136923. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovation through Tradition: The Current Challenges in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 10;23(10):5296. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105296. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628105 Free PMC article.
-
PAMAM-Functionalized Cellulose Nanocrystals with Needle-Like Morphology for Effective Cancer Treatment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jun 22;11(7):1640. doi: 10.3390/nano11071640. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang M., Zhai Y., Ye H., Lv Q., Sun B., Luo C., Jiang Q., Zhang H., Xu Y., Jing Y., et al. High co-loading capacity and stimuli-responsive release based on cascade reaction of self-destructive polymer for improved chemo-photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13:7010–7023. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b02096. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

