Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Hydrochemistry through Integrated Multivariate Analysis: A Case Study in the Urbanized Langat Basin, Malaysia
- PMID: 34071804
- PMCID: PMC8198349
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18115733
Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Hydrochemistry through Integrated Multivariate Analysis: A Case Study in the Urbanized Langat Basin, Malaysia
Abstract
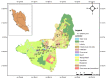
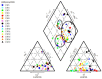
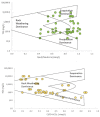
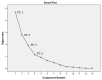
Rapid urbanization and industrial development in the Langat Basin has disturbed the groundwater quality. The populations' reliance on groundwater sources may induce possible risks to human health such as cancer and endocrine dysfunction. This study aims to determine the groundwater quality of an urbanized basin through 24 studied hydrochemical parameters from 45 groundwater samples obtained from 15 different sampling stations by employing integrated multivariate analysis. The abundance of the major ions was in the following order: bicarbonate (HCO3-) > chloride (Cl-) > sodium (Na+) > sulphate (SO42-) > calcium (Ca2+) > potassium (K+) > magnesium (Mg2+). Heavy metal dominance was in the following order: Fe > Mn > Zn > As > Hg > Pb > Ni > Cu > Cd > Se > Sr. Classification of the groundwater facies indicated that the studied groundwater belongs to the Na-Cl with saline water type and Na-HCO3 with mix water type characteristics. The saline water type characteristics are derived from agricultural activities, while the mixed water types occur from water-rock interaction. Multivariate analysis performance suggests that industrial, agricultural, and weathering activities have contributed to groundwater contamination. The study will help in the understanding of the groundwater quality issue and serve as a reference for other basins with similar characteristics.
Keywords: groundwater assessment; groundwater quality; heavy metals; major ions; multivariate statistical analysis; weathering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Evolution of Groundwater Chemistry and Its Controlling Factors in the Huangshui River Basin of Northwestern China, Using Hydrochemistry and Multivariate Statistical Techniques.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 15;18(14):7551. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147551. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299998 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrochemistry and quality appraisal of groundwater in Birr River Catchment, Central Blue Nile River Basin, using multivariate techniques and water quality indices.Environ Monit Assess. 2023 May 11;195(6):655. doi: 10.1007/s10661-023-11198-6. Environ Monit Assess. 2023. PMID: 37165112
-
Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Irrigation Quality Assessment of Shallow Groundwater in the Central-Western Guanzhong Basin, China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Apr 27;16(9):1492. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16091492. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31035576 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and groundwater quality along the Red Sea coast, southern Saudi Arabia.Mar Pollut Bull. 2021 Feb;163:111975. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.111975. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Mar Pollut Bull. 2021. PMID: 33493850
-
Hydrochemistry and groundwater quality in a semiarid calcareous area: an evaluation of major ion chemistry using a stoichiometric approach.Environ Monit Assess. 2018 Oct 18;190(11):641. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-7021-8. Environ Monit Assess. 2018. PMID: 30338491
Cited by
-
Assessment of hydrogeochemistry in groundwater using water quality index model and indices approaches.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 9;9(9):e19668. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19668. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giordano M. Global Groundwater? Issues and Solutions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009;34:153–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.environ.030308.100251. - DOI
-
- Usman U.N., Toriman M.E., Juahir H. Assessment of Groundwater Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques in Terengganu. Sci. Technol. 2015 doi: 10.5923/j.scit.20140403.02. - DOI
-
- Gude V.G. Desalination of deep groundwater aquifers for freshwater supplies–Challenges and strategies. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018;6:87–92. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2017.11.002. - DOI
-
- Sayyed J.A., Bhosle A.B. Analysis of Chloride, Sodium and Potassium in Groundwater Samples of Nanded City in Mahabharata, India. Eur. J. Exp. Bio. 2011;1:74–82.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

