Design and Evaluation of 223Ra-Labeled and Anti-PSMA Targeted NaA Nanozeolites for Prostate Cancer Therapy-Part II. Toxicity, Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution
- PMID: 34071854
- PMCID: PMC8198605
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115702
Design and Evaluation of 223Ra-Labeled and Anti-PSMA Targeted NaA Nanozeolites for Prostate Cancer Therapy-Part II. Toxicity, Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution
Abstract
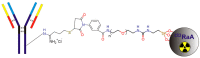
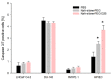
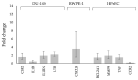
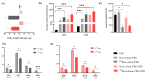
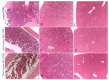
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is a progressive and incurable disease with poor prognosis for patients. Despite introduction of novel therapies, the mortality rate remains high. An attractive alternative for extension of the life of mCRPC patients is PSMA-based targeted radioimmunotherapy. In this paper, we extended our in vitro study of 223Ra-labeled and PSMA-targeted NaA nanozeolites [223RaA-silane-PEG-D2B] by undertaking comprehensive preclinical in vitro and in vivo research. The toxicity of the new compound was evaluated in LNCaP C4-2, DU-145, RWPE-1 and HPrEC prostate cells and in BALB/c mice. The tissue distribution of 133Ba- and 223Ra-labeled conjugates was studied at different time points after injection in BALB/c and LNCaP C4-2 tumor-bearing BALB/c Nude mice. No obvious symptoms of antibody-free and antibody-functionalized nanocarriers cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity was found, while exposure to 223Ra-labeled conjugates resulted in bone marrow fibrosis, decreased the number of WBC and platelets and elevated serum concentrations of ALT and AST enzymes. Biodistribution studies revealed high accumulation of 223Ra-labeled conjugates in the liver, lungs, spleen and bone tissue. Nontargeted and PSMA-targeted radioconjugates exhibited a similar, marginal uptake in tumour lesions. In conclusion, despite the fact that NaA nanozeolites are safe carriers, the intravenous administration of NaA nanozeolite-based radioconjugates is dubious due to its high accumulation in the lungs, liver, spleen and bones.
Keywords: D2B antibodies; PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy; biodistribution; pharmacokinetics; prostate cancer; radium-223; toxicity; zeolite nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design and Evaluation of 223Ra-Labeled and Anti-PSMA Targeted NaA Nanozeolites for Prostate Cancer Therapy-Part I.Materials (Basel). 2020 Sep 2;13(17):3875. doi: 10.3390/ma13173875. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32887308 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies specific to the extracellular domain of prostate-specific membrane antigen: preclinical studies in nude mice bearing LNCaP human prostate tumor.J Nucl Med. 2003 Apr;44(4):610-7. J Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 12679407
-
Preclinical Efficacy of a PSMA-Targeted Thorium-227 Conjugate (PSMA-TTC), a Targeted Alpha Therapy for Prostate Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Apr 15;26(8):1985-1996. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2268. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31831560
-
Targeted Radionuclide Therapy of Prostate Cancer-From Basic Research to Clinical Perspectives.Molecules. 2020 Apr 10;25(7):1743. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071743. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32290196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radioimmunotherapy of Metastatic Prostate Cancer with ¹⁷⁷Lu-DOTAhuJ591 Anti Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Specific Monoclonal Antibody.Curr Radiopharm. 2016;9(1):44-53. doi: 10.2174/1874471008666150313114005. Curr Radiopharm. 2016. PMID: 25771365 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and in vitro evaluation of 223Ra/99mTc-loaded spherical nano-hydroxyapatite in bone tumor therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024 Jul 14;19(17):1557-1567. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2365127. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39011932 Free PMC article.
-
PSMA-Targeted Nanotheranostics for Imaging and Radiotherapy of Prostate Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;16(2):315. doi: 10.3390/ph16020315. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Curies' element: state of the art and perspectives on the use of radium in nuclear medicine.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2023 Nov 10;8(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s41181-023-00220-4. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2023. PMID: 37947909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unleashing novel horizons in advanced prostate cancer treatment: investigating the potential of prostate specific membrane antigen-targeted nanomedicine-based combination therapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1265751. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1265751. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37795091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiolabeled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: radiopharmacy in the era of nanotechnology.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2022 Apr 25;7(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s41181-022-00161-4. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2022. PMID: 35467307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chowdhury S., Bjartell A., Lumen N., Maroto P., Paiss T., Gomez-Veiga F., Birtle A., Kramer G., Kalinka E., Spaëth D., et al. Real-World Outcomes in First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: The Prostate Cancer Registry. Target. Oncol. 2020;15:301–315. doi: 10.1007/s11523-020-00720-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Czerwińska M., Bilewicz A., Kruszewski M., Wegierek-Ciuk A., Lankoff A., Fracasso G., Pruszyński M., Bilewicz A., Kruszewski M., Majkowska-Pilip A., et al. Targeted radionuclide therapy of prostate cancer-from basic research to clinical perspectives. Molecules. 2020;25:1743. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kratochwil C., Giesel F.L., Stefanova M., Benesova M., Bronzel M., Afshar-Oromieh A., Mier W., Eder M., Kopka K., Haberkorn U. PSMA-targeted radionuclide therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with 177Lu-Labeled PSMA-617. J. Nucl. Med. 2016;57:1170–1176. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.171397. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sadaghiani M.S., Sheikhbahaei S., Werner R.A., Pienta K.J., Pomper M.G., Solnes L.B., Gorin M.A., Wang N.-Y., Rowe S.P. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Effectiveness and Toxicities of Lutetium-177–labeled Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen–targeted Radioligand Therapy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.03.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

