The Effect of a Multi-Ingredient Pre-Workout Supplement on Time to Fatigue in NCAA Division I Cross-Country Athletes
- PMID: 34071868
- PMCID: PMC8228073
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13061823
The Effect of a Multi-Ingredient Pre-Workout Supplement on Time to Fatigue in NCAA Division I Cross-Country Athletes
Abstract
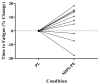
This investigation aimed to determine the effect of a multi-ingredient pre-workout supplement (MIPS) on heart rate (HR), perceived exertion (RPE), lactate concentration, and time to fatigue (TTF) during a running task to volitional exhaustion. Eleven NCAA Division I cross-country runners (20 ± 2 year; height: 171 ± 14 cm; weight: 63.5 ± 9.1 kg) participated in this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study. Bayesian statistical methods were utilized, and parameter estimates were interpreted as statistically significant if the 95% highest-density intervals (HDIs) did not include zero. TTF was increased in the MIPS condition with a posterior Meandiff = 154 ± 4.2 s (95% HDI: -167, 465) and a 0.84 posterior probability that the supplement would increase TTF relative to PL. Blood lactate concentration immediately post-exercise was also higher in the MIPS condition compared to PL with an estimated posterior Meandiff = 3.99 ± 2.1 mmol (95% HDI: -0.16, 7.68). There were no differences in HR or RPE between trials. These findings suggest that a MIPS ingested prior to sustained running at lactate threshold has an 84% chance of increasing TTF in highly trained runners and may allow athletes to handle a higher level of circulating lactate before reaching exhaustion.
Keywords: acute; caffeine; endurance; ergogenic aid; multi-ingredient pre-workout supplement; running performance; sports nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bloomer R.J., Farney T.M., Trepanowski J.F., McCarthy C.G., Canale R.E., Schilling B.K. Comparison of pre-workout nitric oxide stimulating dietary supplements on skeletal muscle oxygen saturation, blood nitrate/nitrite, lipid peroxidation, and upper body exercise performance in resistance trained men. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010;7:16. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-7-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cameron M., Camic C.L., Doberstein S., Erickson J.L., Jagim A.R. The acute effects of a multi-ingredient pre-workout supplement on resting energy expenditure and exercise performance in recreationally active females. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018;15:1. doi: 10.1186/s12970-017-0206-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collins P.B., Earnest C.P., Dalton R.L., Sowinski R.J., Grubic T.J., Favot C.J., Coletta A.M., Rasmussen C., Greenwood M., Kreider R.B. Short-Term Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Pre-Workout Beverage on Exercise Performance and Recovery. Nutrients. 2017;9:823. doi: 10.3390/nu9080823. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

